108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小细胞肺癌患者血浆中 EGFR ,KRAS ,BRAF ,PTEN 和 PIK3CA 突变
Authors Lu HY, Qin J, Han N, Lei L, Xie F, Li C
Received 12 December 2017
Accepted for publication 19 March 2018
Published 20 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2217—2226
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S159612
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive and deadly neuroendocrine
tumor derived from bronchial epithelial cells. Although it results in a 95%
mortality rate, the development of targeted therapies for SCLCs has lagged
behind. The aim of this study is to better research mutation characteristics of
SCLC and identify potential biomarkers for target therapy.
Methods: We utilized high- resolution melting analysis to identify the mutations
in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR ), Kirsten rat
sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS ), v-raf murine
sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF ), phosphatase
and tensin homolog (PTEN ), and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
catalytic (PIK3CA ) from the blood. A cohort
of 99 SCLC patients including 44 limited-stage disease patients and 55
extensive-stage disease patients were prospectively collected.
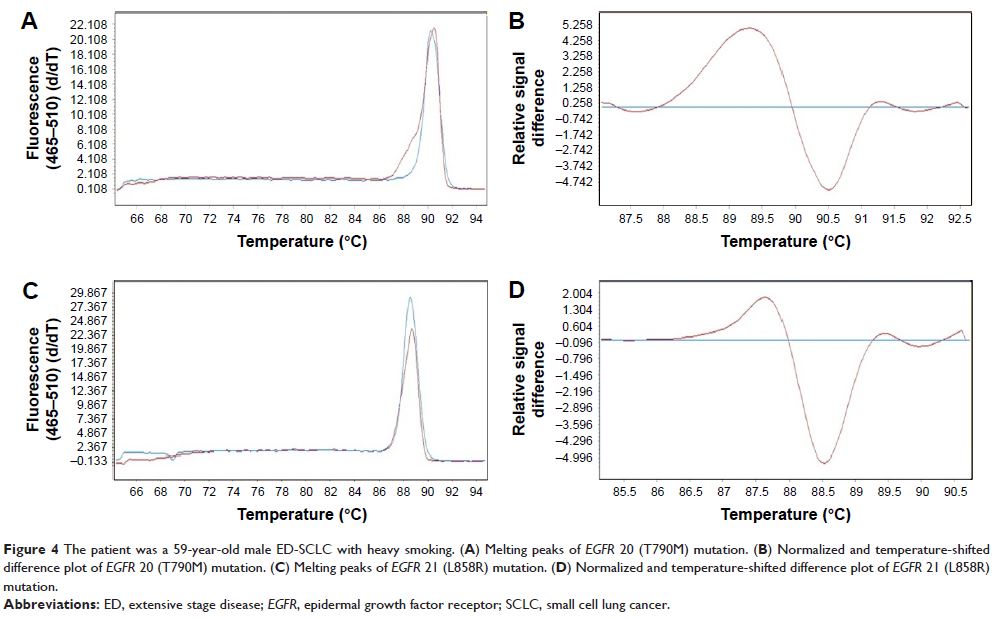
Results: EGFR 18 (G719X) mutation was
found in 5 patients, EGFR 19 (del)
mutation in 2, EGFR 20
(T790M) in 3, EGFR 21
(L858R) in 2, KRAS 2 (G13D)
in 5, BRAF 15 (V600E) in 1, PIK3CA 9 (E542K) in 1, and no
mutations in PTEN 5 (R130G), PTEN 6 (R173C), PTEN 8 (T319fs*1), and PIK3CA 20 (H1047R) were
identified. Among these patients, two harbored EGFR double
mutation, one patient with EGFR double
mutation and KRAS 2 (G13D) mutation.
Conclusion: The mutation form of EGFR may
differ from lung adenocarcinoma, and mutations of KRAS , BRAF , and PIK3CA were rare in SCLC.
These results aided us in comprehensively analyzing genetic features and laid
the foundation for exploring the possibility of target therapy.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, small cell lung cancer, plasma,
high-resolution melting