108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ITGA7 发挥肿瘤抑制剂的功用并调节乳腺癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Bhandari A, Xia E, Zhou Y, Guan Y, Xiang J, Kong L, Wang Y, Yang F, Wang O, Zhang X
Received 20 December 2017
Accepted for publication 14 March 2018
Published 1 May 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 969—976
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S160379
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Background: Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women and the underlying
mechanism of breast cancer cell metastasis is still far from uncover. Integrin subunit alpha 7 (ITGA7 ) is a functioning protein.
It has been detected in many malignancies. But the function of ITGA7 in breast cancer is not
clear. Our aim is to explore ITGA7 expression
and its role in breast cancer.
Methods: Real-time PCR was performed to determine ITGA7 expression in BC
tissues and normal adjacent tissues. The specific functions of ITGA7 in breast cancer cell
lines (MDA-MB-231 and BT-549) transfected with small interfering RNA were
determined through migration, invasion assays. Western blot assays were
performed to determine the expression of c-met and vimentin.
Results: ITGA7 was down-regulated in breast cancer tissues compared to the
adjacent normal tissues (T:N =7.68±27.38: 41.01± 31.47, P <0.001) and this observation
was consistent with the TCGA cohort (T:N =4.51±0.45:5.40±0.61, P <0.0001). In vitro experiments
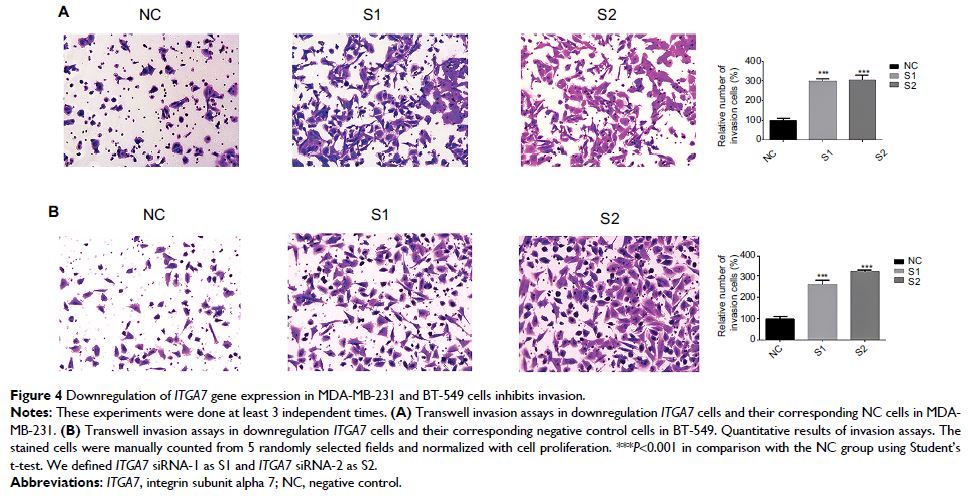
showed that knocking down ITGA7 significantly
inhibited the migration and invasion of the breast cancer cell lines
(MDA-MB-231 and BT-549). Meanwhile, knockdown of ITGA7 promoted c-met and
vimentin expression, which may induce invasion and migration.
Conclusion: ITGA7 plays an important
tumorigenic function and acts as a suppress gene in breast cancer. Our findings
indicate that ITGA7 was the
gene associated with breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, ITGA7 , migration,
invasion