108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:通过基于纳米粒子的 miRNA 递送系统来抑制 miR-221,用于肝细胞癌治疗和诊断(作为潜在生物标志物)
Authors Li F, Wang F, Zhu C, Wei Q, Zhang T, Zhou YL
Received 22 November 2017
Accepted for publication 17 February 2018
Published 13 April 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2295—2307
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S157805
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yashdeep Phanse
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: MicroRNA-221(miR-221) is frequently dysregulated in cancer. The
purpose of this study was to explore whether miR-221 can be used as a potential
diagnostic marker or therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC).
Methods: In this study, we investigated whether miR-221
expression was associated with clinicopathological characteristics and
prognosis in HCC patients, and we developed a nanoparticle-based miRNA delivery
system and detected its therapeutic efficacy in vitro and in vivo.
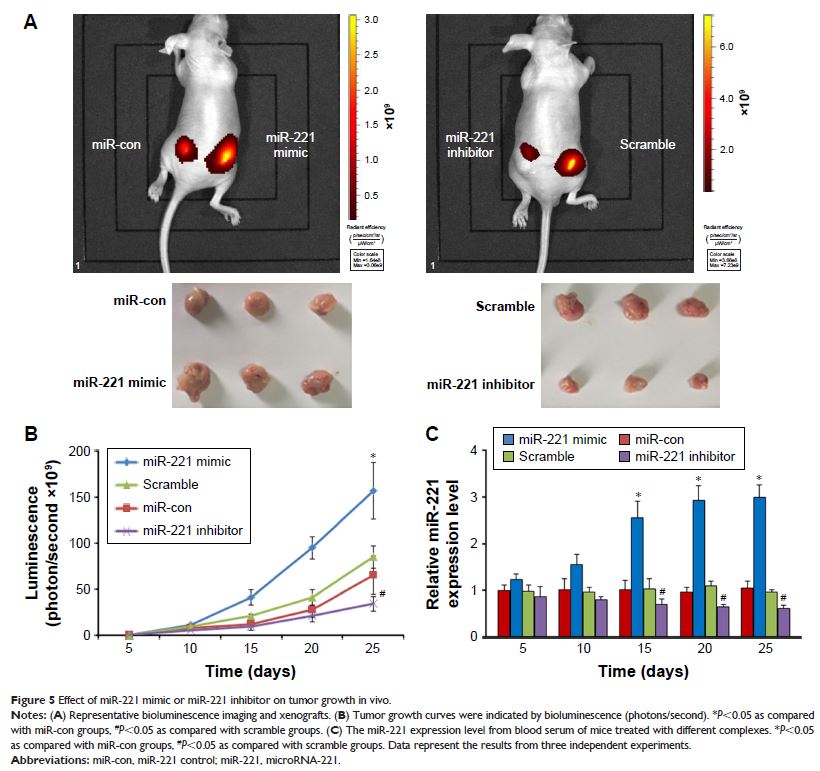
Results: We found that miR-221 was upregulated in HCC tissues,
cell lines and blood of HCC patients. Upregulated miR-221 was associated with
clinical TNM stage and tumor capsular infiltration, and showed poor prognosis,
suggesting that its suppression could serve as an effective approach for
hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Treatment of HCC cells with
nanoparticle/miR-221 inhibitor complexes suppressed their growth, colony
formation ability, migration and invasion. In vivo, the growth of the tumors
treated by the nanoparticle/miR-221 inhibitor complexes were significantly less
than those treated by the nanoparticle/miRNA scramble complexes. In addition,
circulating miR-221 may act as a potential tumor biomarker for early diagnosis
of HCC, and combined serum miR-221 and AFP detection gave a better performance
than individual detection in early diagnosis of HCC.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that a nanoparticle-based miRNA
delivery system could potentially serve as a safe and effective treatment and
miR-221 could also be a potential diagnostic marker for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, nanoparticle, miR-221, biomarker, therapeutic target