108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

EGFR 突变型非小细胞肺癌患者脑转移的多种治疗方式
Authors Wang HY, Yu X, Fan Y, Jiang Y
Received 9 November 2017
Accepted for publication 4 March 2018
Published 13 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2149—2155
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156570
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: There are many controversies concerning the best management of epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
patients with brain metastases (BMs). The use of upfront EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitors (TKIs) and the withholding of local therapies or upfront radiation
therapies (RTs) remain controversial. Available treatment options include local
therapies such as whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT), stereotactic
radiosurgery (SRS) and surgery, EGFR-TKIs, and chemotherapy. However, the
optimal management of combination therapies is still under consideration.
Patients and
methods: A total of 45 EGFR-mutated NSCLC
patients with BMs were included. All patients successively received EGFR-TKIs,
RT (WBRT or SRS), and chemotherapy between 2010 and 2015 at Zhejiang Cancer
Hospital. Patient follow-up was conducted by telephone until February 2017. The
treatment response was evaluated, and survival data were collected and analyzed
by Kaplan–Meier analysis and the Cox regression method.
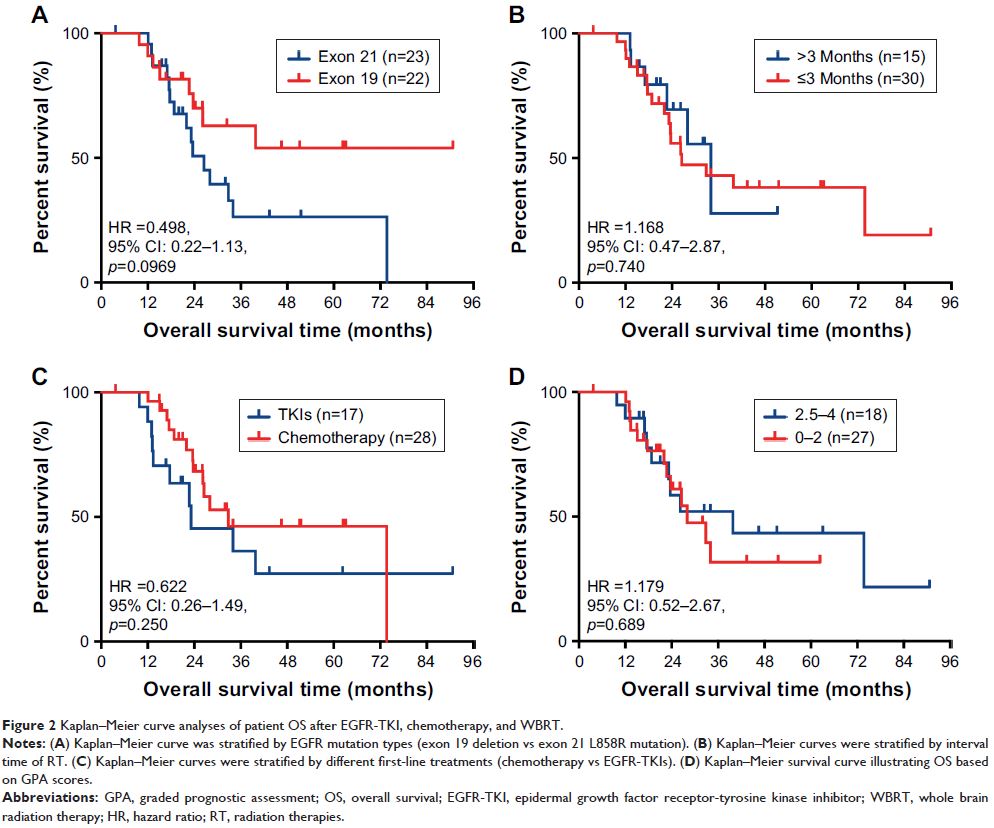
Results: The median overall survival (OS) was 28 months. Patients with the exon
19 deletion showed the strongest trend toward a longer median OS compared to
patients with the exon 21 L858R mutation (not reached vs 26.5 months, P =0.0969). There was no difference
in OS between the upfront RT group and the deferral group (26.5 vs 28
months, P =0.57), and similar results were
found between the first-line chemotherapy group and the EGFR-TKI group (28 vs
23.2 months, P =0.499). In multivariate
analysis, the prognosis correlated with EGFR mutation type (P =0.017).
Conclusion: EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with BM benefited from the combination
and sequential therapies of EGFR-TKIs, chemotherapy, and RTs. Patients with the
EGFR exon 19 deletion may have a better OS. However, the optimal timing of RT
interval remains to be explored.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, tyrosine kinase inhibitors,
brain metastases, non-small-cell lung cancer, pemetrexed, whole-brain radiation
therapy