108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SIRT3 在各种癌症中表达的预后和临床病理价值:一个系统综述和荟萃分析
Authors Zhou Y, Cheng S, Chen S, Zhao Y
Received 22 November 2017
Accepted for publication 5 March 2018
Published 13 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2157—2167
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157836
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: Several studies have explored the prognostic value of sirtuin 3 (SIRT3)
in various cancers, but obtained inconsistent results. The current systematic
review and meta-analysis was conducted to investigate the association between
SIRT3 expression and prognosis in various cancers.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library were
comprehensively retrieved by the end of September 29, 2017. All the relevant
studies were checked and included in the meta-analysis if they met the
inclusion criteria.
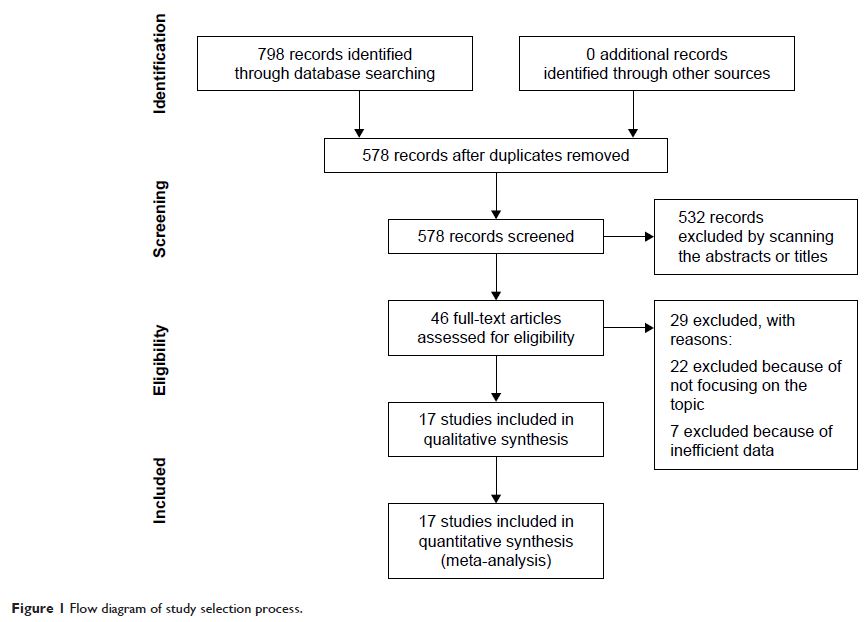
Results: A total of 17 studies involving 2,865 patients were included in
the systematic review and meta-analysis. The results indicated that SIRT3
expression was not significantly associated with overall survival (OS) (hazard
ratio [HR]=0.87, 95% CI=0.59–1.29, P =0.50) and
disease-free survival (HR=0.87, 95% CI=0.57–1.31, P =0.50) in total various cancers.
However, significant relationship between SIRT3 expression and OS in specific
cancers was detected, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (HR=0.48,
95% CI=0.26–0.89, P =0.019),
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (HR=0.56, 95% CI=0.42–0.74, P <0.001), pancreatic carcinoma
(PC) (HR=0.55, 95% CI=0.30–1.00, P =0.049), renal
cell carcinoma (RCC) (HR=0.13, 95% CI=0.02–0.98, P =0.048), breast cancer (BC)
(HR=2.53, 95% CI=1.83–3.67, P <0.001), colon
cancer (CC) (HR=1.87, 95% CI=1.12–3.26, P =0.022) and
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (HR=2.20, 95% CI=1.38–3.50, P =0.001). Moreover, SIRT3
expression was obviously associated with tumor size (odds ratio [OR]=1.41, 95%
CI=1.02–1.94, P =0.04), tumor
differentiation (OR=1.52, 95% CI=1.08–2.16, P =0.02)
and clinical stage (OR=2.07, 95% CI=1.23–3.46, P =0.01)
in HCC.
Conclusion: SIRT3 was distinctly related to the OS in specific cancers. SIRT3 was an
unfavorable prognostic factor in BC, CC and NSCLC; however, it was also a
favorable prognostic factor in CLL, HCC, PC and RCC, especially in HCC.
Keywords: SIRT3, cancer, prognostic, clinicopathological, overall survival, meta-analysis