108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对甲磺酸倍他司汀片在前庭阵发性房颤治疗中作为奥卡西平和卡马西平的增强剂的随机试验
Authors Xue H, Xiang W, Yu Y, Liu G, Chong Y, Zhou J
Received 5 December 2017
Accepted for publication 14 February 2018
Published 12 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 837—843
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S158888
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Dragan Hrncic
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios Panos
Background: Vestibular paroxysmia (VP) is a rare episodic peripheral
vestibular disorder. This study was conducted to compare the efficacy and
acceptability of carbamazepine (CBZ) plus betahistine mesilate tablets (BMT)
(CBZ+BMT) and oxcarbazepine (OXC) plus BMT (OXC+BMT) in treating VP, and
investigated whether the synergistic effect could be increased along with the
increased dose of BMT.
Methods: VP patients were recruited and randomly assigned
to receive CBZ+BMT or OXC+BMT. The doses of CBZ and OXC were set to 200 and
300 mg/time, twice daily, respectively. The doses of BMT were set to 12
and 18 mg/time, twice daily. Half of the patients in each group received
BMT 12 mg/time and the other half received BMT 18 mg/time. The
treatment was continued for 12 weeks. The vertigo frequency, vertigo score,
vertigo duration, response rate, and drug-related side effects were analyzed.
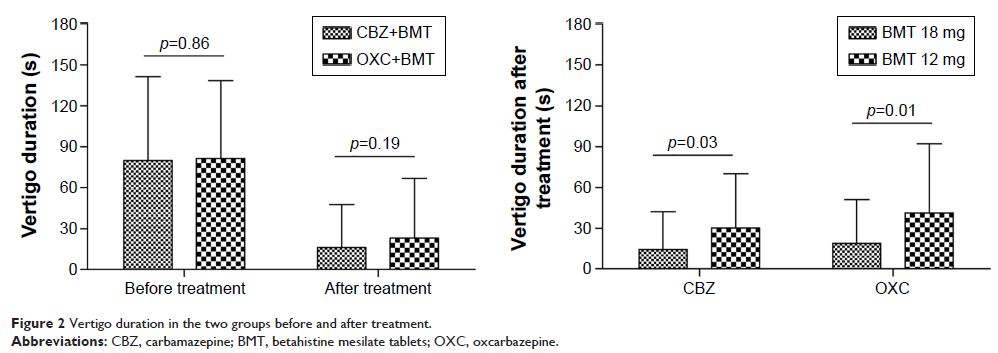
Results: In total, 92 patients in the CBZ+BMT group and
93 patients in the OXC+BMT group completed this trial. After 12 weeks of
treatment, the two groups had similar average vertigo frequency, average
vertigo score, average vertigo duration, and response rate. But the incidence
of side effects was significantly higher in the CBZ+BMT group than in the
OXC+BMT group (p =0.04). Subgroup analysis found
that patients receiving BMT (18 mg) had greater reductions in average
vertigo frequency, average vertigo duration, and average vertigo score, and
higher response rates than patients receiving BMT (12 mg).
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that OXC+BMT may be
suitable as an alternative method in VP patients with CBZ hypersensitivity, and
the synergistic effect could be increased along with the increased dose of BMT.
Keywords: vestibular
paroxysmia, betahistine mesilate tablets, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine