108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

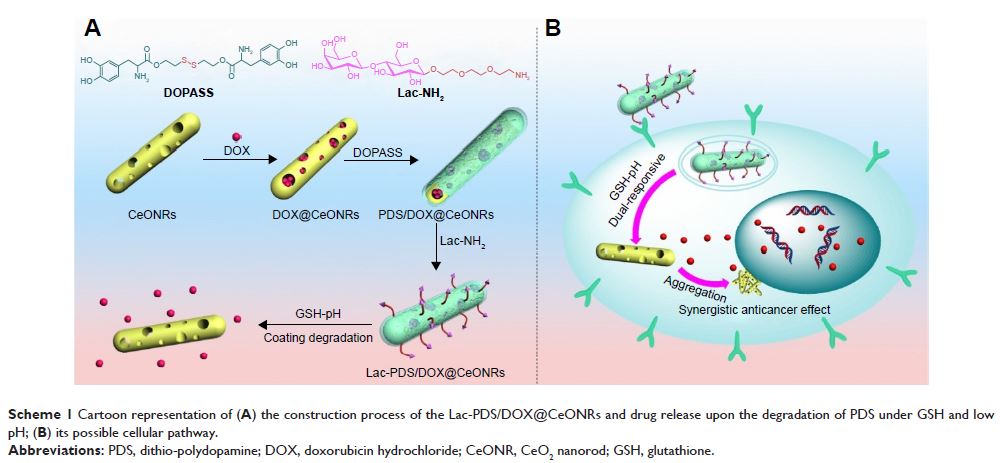
用于双重响应性靶向和协同药物递送系统的二硫 - 聚多巴胺涂覆的多孔 CeO2 纳米棒
Authors Zhang Y, Wu X, Hou C, Shang K, Yang K, Tian ZM, Pei Z, Qu Y, Pei Y
Received 29 September 2017
Accepted for publication 26 January 2018
Published 12 April 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2161—2173
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S152002
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Objective: The aim was to produce the
first report of assembling degradable stimuli-responsive dithio-polydopamine
coating with a cancer target unit for synergistic and targeted drug delivery.
Methods: A multifunctional drug delivery system was
constructed by coating a dual-responsive dithio-polydopamine (PDS) on porous
CeO2 nanorods and subsequent conjugation of lactose
derivative, where the PDS was formed by self-polymerization of dithio-dopamine
(DOPASS).
Results: The multifunctional drug delivery system
displayed excellent cancer targeted ability resulting from the conjugation of
lactose derivative, which could specifically recognize the overexpressed
asialoglycoprotein receptors on the surface of HepG2 cells. It also showed a
dual-responsive property of glutathione and pH, achieving controllable drug release
from the cleavage of disulfide bond and subsequent degradation of PDS in cancer
cells. Moreover, the degradation of PDS led to the exposure of CeO2 nanorods, which has a synergistic anticancer
effect due to its cytotoxicity to cancer cells.
Conclusion: This work presents a good example of a rational
design towards synergistic and targeted DDS for cancer chemotherapies.
Keywords: degradable
polydopamine, cerium oxide nanoparticles, dual-responsiveness, targeted drug
delivery, synergistic anticancer