109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

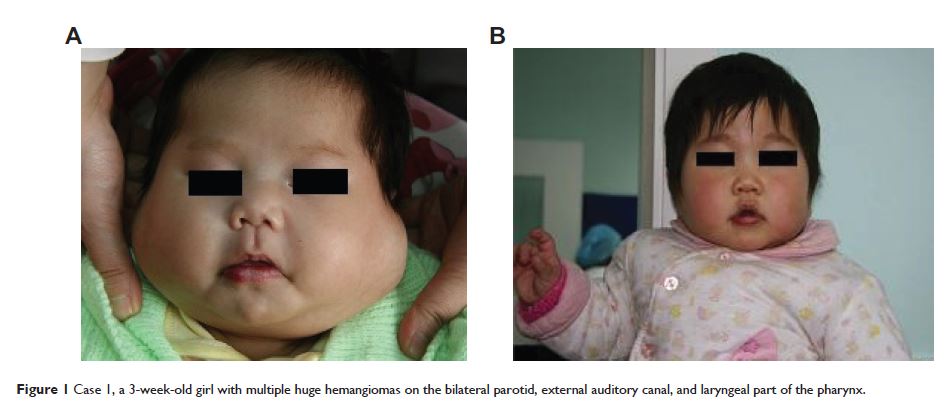
用干扰素 α2a 治疗令人担忧的婴幼儿头部和颈部血管瘤:对 11 例患者的连续临床研究
Authors Zhang L, Zheng JW, Yuan WE
Published Date February 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 723—727
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S67682
Received 13 May 2014, Accepted 20 June 2014, Published 4 February 2015
Objective: To evaluate
the efficacy and adverse effects of interferon-α2a in the treatment of alarming
infantile hemangiomas in the head and neck region.
Patients and methods: From
January 2009–December 2010, a subcutaneous injection of interferon-α2a was
applied to eleven infants with giant multifocal or segmental hemangiomas at a
dose of 3 million units/m2 per day. All patients did not respond to
propranolol or corticosteroids. The age at initiation of interferon-α2a therapy
ranged from 3 days to 8 months (median: 4 months). The duration
of therapy ranged from 2–4.5 months (median: 3 months). Eight
patients received medication for 3 months, one patient for
4.5 months, and two patients for 2 months.
Results: Nine patients had a
reduction in tumor mass of 95%; two patients’ tumors decreased in size by 75%.
The overall response rate was 100%. The main adverse effects included fever,
diarrhea, and anorexia, which resolved after stopping the medication. No
serious adverse effect was observed.
Conclusion: Short-term
treatment with interferon-α2a can be used as a safe and effective treatment for
alarming infantile hemangiomas that are resistant to propranolol or
corticosteroids, and that endanger the proper functioning of the affected organ
or the patient’s life.
Keywords: hemangioma,
interferon-α, head and neck, adverse effect