108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在七氟醚预处理介导的心脏保护中上调血管内皮生长因子受体1的有利作用
Authors Qian B, Yang Y, Yao Y, Liao Y, Lin Y
Received 15 January 2018
Accepted for publication 1 March 2018
Published 6 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 769—776
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S162577
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Purpose: Sevoflurane preconditioning (SPC) can provide myocardial protective
effects similar to ischemic preconditioning. However, the exact mechanism of
SPC remains unclear. Previous studies indicate that vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 1 (VEGFR-1) is involved in ischemic preconditioning-mediated
cardioprotection. This study was designed to determine the significance of
VEGFR-1 signaling in SPC-mediated cardioprotection.
Materials and
methods: Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion
(I/R) rat model was established using the Langendorff isolated heart perfusion
apparatus. Additionally, after 15 min of baseline equilibration, the isolated
hearts were pretreated with 2.5% sevoflurane, 2.5% sevoflurane+MF1 10 µmol/L,
or 2.5% sevoflurane+placental growth factor 10 µmol/L, and then subjected to 30
min of global ischemia and 120 min of reperfusion. The changes in hemodynamic
parameters, myocardial infarct size, and the levels of creatine kinase-MB,
lactate dehydrogenase, cardiac troponin-I, tumor necrosis factor-α, and
interleukin 6 in the myocardium were evaluated.
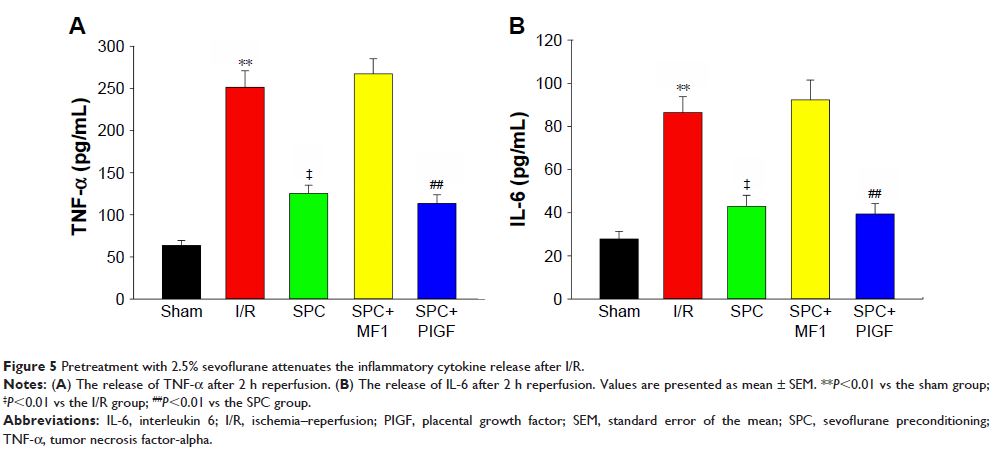
Results: Compared to the I/R group, pretreatment with 2.5% sevoflurane
significantly improved the cardiac function, limited myocardial infarct size,
reduced cardiac enzyme release, upregulated VEGFR-1 expression, and decreased
inflammation. In addition, the selective VEGFR-1 agonist, placental growth
factor, did not enhance the cardioprotection and anti-inflammation effects of
sevoflurane, while the specific VEGFR-1 inhibitor, MF1, completely reversed
these effects.
Conclusion: Our data have demonstrated that 2.5% sevoflurane preconditioning
alleviates heart I/R injury, which is probably mediated by the
anti-inflammatory property and upregulation of VEGFR-1.
Keywords: sevoflurane, preconditioning, ischemic–reperfusion injury, vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 1, anti-inflammatory