108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-542-3p 的下调通过在肝细胞癌中激活 TGF-/Smad 信号传导来促进癌症转移
Authors Zhang T, Liu W, Meng W, Zhao H, Yang Q, Gu SJ, Xiao CC, Jia CC, Fu BS
Received 18 October 2017
Accepted for publication 16 January 2018
Published 5 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1929—1939
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154416
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Introduction: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) accounts for more than 90% of primary liver cancer. Although
great progress has been made on HCC molecular mechanism and therapy techniques,
the prognosis of HCC patient is poor due to high metastasis and
recurrence.
Materials and
methods: Expression of miR-542-3p was
quantified by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The role of miR-542-3p in
HCC metastasis was examined using transwell and 3D-culture assay. qRT-PCR,
Western blotting and luciferase reporter assay were used to elucidate the
mechanisms of miR-542-3p-mediated cancer metastasis.
Results and
Conclusion: In the research, we found that
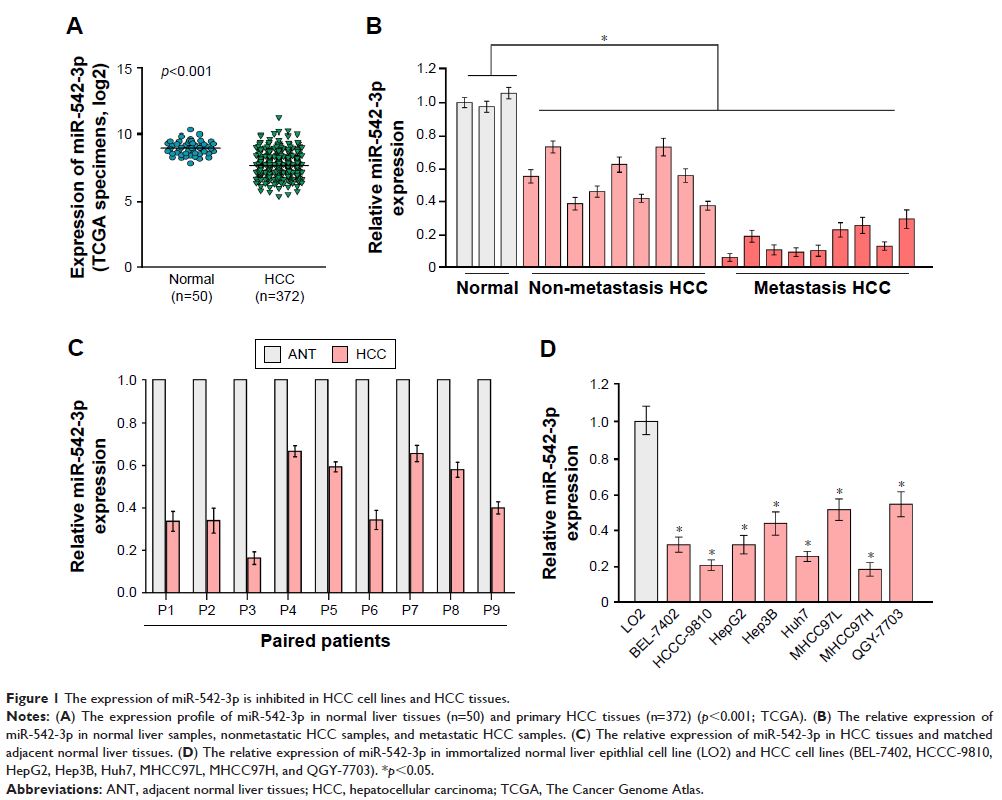
miR-542-3p is decreased in HCC cell lines and tissues, and downregulation of
miR-542-3p enhances, while upregulation suppresses HCC cell invasion ability.
Further assay demonstrated that miR-542-3p can directly target TGF-β1 3'
untranslated region (3'UTR) to influence TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, and
suppression of miR-542-3p can hyperactivate TGF-β/Smad pathway and further to
promote Epithelial-Mesenchyme Transition (EMT) and induce poor prognosis.
Lastly, the clinical correlation analysis illustrated that miR-542-3p is
negatively related with the activity of TGF-β1. In summary, our results find
that miR-542-3p takes an important role on HCC progression and provide more
evidence of microRNAs (miRNAs) for cancer therapy.
Keywords: microRNA, HCC, TGF-β, EMT