108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
99mTc 标记的肌醇六磷酸钠和氯化亚锡注射液可准确检测早期乳腺癌腋窝前哨淋巴结:一项随机对照研究
Authors Yang S, Bao W, Bai X, Gao C, Zhang B, Jiang Z
Received 26 October 2017
Accepted for publication 4 January 2018
Published 4 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1891—1898
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155265
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ru Chen
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
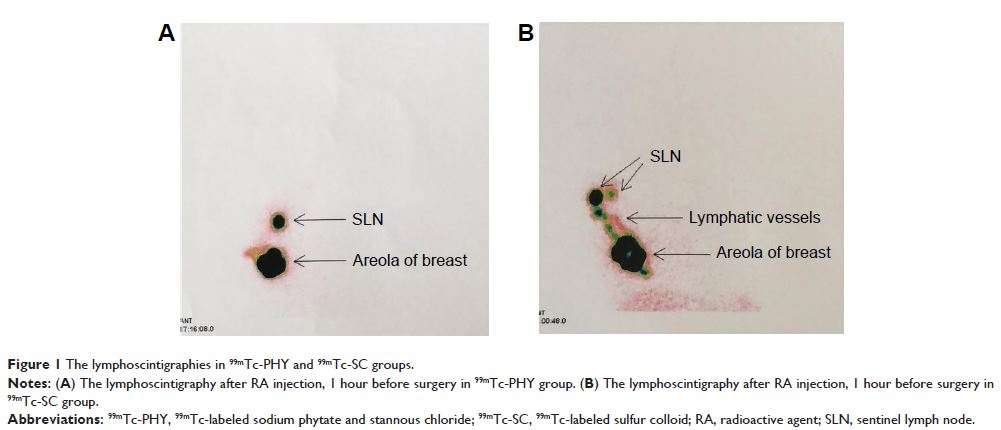
Aim: The aim of this study
was to assess the sentinel lymph node (SLN) detection rate and accuracy
of 99mTc-labeled sodium
phytate and stannous chloride (99mTc-PHY) injection
versus 99mTc-labeled sulfur
colloid (99mTc-SC) injection in
sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in patients with early stage breast cancer.
Methods: A total of 146 consecutive female patients with early stage breast cancer were recruited in this open-labeled, randomized, controlled study. SLNB was conducted on all patients, and 99mTc-PHY or 99mTc-SC was used as the radioactive agent (RA). Axillary lymph node dissections were performed in all patients post SLN dissections.
Results: The detection rate of 99mTc-PHY group was higher compared with that of 99mTc-SC group (p =0.023), but no difference in the detection rate by dye alone (p =0.190) or by RAs alone (p =0.615) was found between the two groups, and the number of identified SLNs (p =0.100), number of identified SLNs by dye alone (p =0.161), and number of identified SLNs by RA alone (p =0.242) were similar between the two groups. In addition, the sensitivity, specificity, false-negative rate, false-positive rate, and accuracy rate of SLNB showed no difference between 99mTc-PHY and 99mTc-SC groups (sensitivity: p =0.645; specificity: p =0.511; false-negative rate: p =0.645; false-positive rate: p =0.511; accuracy rate: p =0.464).
Conclusion: Our study revealed that 99mTc-PHY was qualified to be a convincing radiopharmaceutical in SLNB.
Keywords: breast cancer, sentinel lymph node biopsy, 99mTc, sodium phytate, stannous chloride, detection rate
Methods: A total of 146 consecutive female patients with early stage breast cancer were recruited in this open-labeled, randomized, controlled study. SLNB was conducted on all patients, and 99mTc-PHY or 99mTc-SC was used as the radioactive agent (RA). Axillary lymph node dissections were performed in all patients post SLN dissections.
Results: The detection rate of 99mTc-PHY group was higher compared with that of 99mTc-SC group (p =0.023), but no difference in the detection rate by dye alone (p =0.190) or by RAs alone (p =0.615) was found between the two groups, and the number of identified SLNs (p =0.100), number of identified SLNs by dye alone (p =0.161), and number of identified SLNs by RA alone (p =0.242) were similar between the two groups. In addition, the sensitivity, specificity, false-negative rate, false-positive rate, and accuracy rate of SLNB showed no difference between 99mTc-PHY and 99mTc-SC groups (sensitivity: p =0.645; specificity: p =0.511; false-negative rate: p =0.645; false-positive rate: p =0.511; accuracy rate: p =0.464).
Conclusion: Our study revealed that 99mTc-PHY was qualified to be a convincing radiopharmaceutical in SLNB.
Keywords: breast cancer, sentinel lymph node biopsy, 99mTc, sodium phytate, stannous chloride, detection rate