108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
D-柠檬烯通过诱导肺癌中的自噬和细胞凋亡显示出其抗肿瘤活性
Authors Yu X, Lin H, Wang Y, Lv W, Zhang S, Qian Y, Deng X, Feng N, Yu H, Qian B
Received 1 November 2017
Accepted for publication 6 February 2018
Published 4 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1833—1847
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155716
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Purpose: D-limonene is a
plant extract with widespread application, and it has been recently reported to
have antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects on cancer cells. However, the
mechanisms by which D-limonene achieves these effects, especially in lung
cancer, are not entirely clear. Therefore, the goal of this study was to
examine the effects of D-limonene on lung cancer and explore its mechanisms of
action.
Methods: We examined the therapeutic effects of D-limonene on lung cancer cells and in a xenograft animal model by characterizing its effects on the pathways of apoptosis and autophagy. Cell proliferation was measured using the Cell Counting Kit-8, and apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric analysis. Levels of LC3 puncta, an autophagy marker, were analyzed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Autophagy and apoptosis-related gene expression were assessed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot.
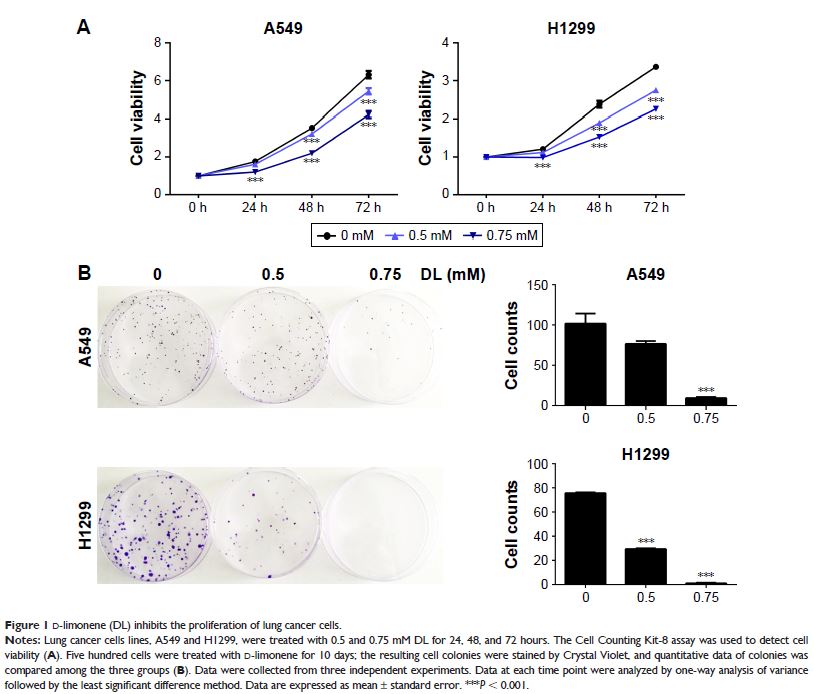
Results: D-limonene inhibited the growth of lung cancer cells and suppressed the growth of transplanted tumors in nude mice. Expression of apoptosis and autophagy-related genes were increased in tumors after treatment with D-limonene. Furthermore, the use of chloroquine, an autophagy inhibitor, and knockdown of the atg5 gene, suppressed the apoptosis induced by D-limonene.
Conclusion: D-limonene may have a therapeutic effect on lung cancer as it can induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells by promoting autophagy.
Keywords: D-limonene, lung cancer, apoptosis, autophagy
Methods: We examined the therapeutic effects of D-limonene on lung cancer cells and in a xenograft animal model by characterizing its effects on the pathways of apoptosis and autophagy. Cell proliferation was measured using the Cell Counting Kit-8, and apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric analysis. Levels of LC3 puncta, an autophagy marker, were analyzed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Autophagy and apoptosis-related gene expression were assessed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot.
Results: D-limonene inhibited the growth of lung cancer cells and suppressed the growth of transplanted tumors in nude mice. Expression of apoptosis and autophagy-related genes were increased in tumors after treatment with D-limonene. Furthermore, the use of chloroquine, an autophagy inhibitor, and knockdown of the atg5 gene, suppressed the apoptosis induced by D-limonene.
Conclusion: D-limonene may have a therapeutic effect on lung cancer as it can induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells by promoting autophagy.
Keywords: D-limonene, lung cancer, apoptosis, autophagy