108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳腺癌术后放疗致急性皮炎的发病率及其影响因素
Authors Ding J, Guo Y, Li Q, Chen J, Hu P, Liu Q, Cao Y, Wu J
Received 4 November 2017
Accepted for publication 14 February 2018
Published 23 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1665—1670
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156066
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: To investigate the incidence of skin acute reaction and its
influencing factors in postoperative breast cancer radiotherapy patients.
Methods: One hundred and seventy three cases of breast cancer patients
treated with postoperative radiotherapy were consecutively enrolled from June
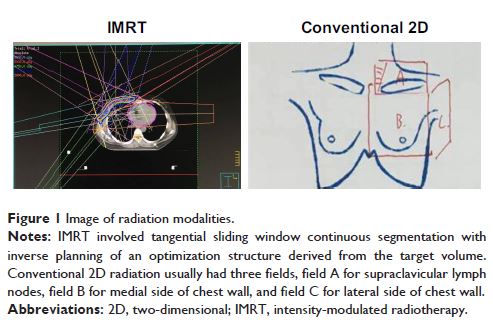
1, 2016 to July 31, 2017 in our breast cancer center. Irradiation technology
includes conformal intensity-modulated radiotherapy and a conventional
two-dimensional one with conventional fraction. Any acute radiation dermatitis
was recorded and the influencing factors were analyzed at the end of the
radiation treatment.
Results: Radiotherapy-induced acute dermatitis in patients with
breast-conserving surgery was relatively mild. Among the 173 patients, 33 cases
had no obvious changes in the skin (grade 0); 121 cases had grade 1 skin
reactions, manifested as local dark erythema and dry peeling; 29 cases had
grade 2 skin reactions, characterized by edema, hyperemia, or erosion part; no
grade 3 cases of skin reactions were observed. The incidence of grade 0, grade
1, and grade 2 reactions in all patients was 19.1%, 69.9%, and 11.0%,
respectively. The severity of skin acute reaction is independent of the tumor
sites, molecular subtypes, patients’ age, and irradiation modalities, but it
depends on the surgical types, fields treated, and planned total radiation.
There is a trend favoring no chemotherapy over chemotherapy, though p -value is 0.074.
Conclusion: Skin acute reaction in postoperative radiotherapy breast cancer
patients is generally common but mild, and there are quite a few patients who
need interruption or cessation of the radiotherapy process. The patients need
to be well informed and made aware that any skin reaction will likely be mild,
especially for the breast-conserving patients.
Keywords: breast neoplasm, radiotherapy, skin acute reaction, intensity modulated
radiotherapy (IMRT)