108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ZW10 相互作用蛋白对肺癌预后价值的生物信息学分析
Authors Yuan W, Xie S, Wang M, Pan S, Huang X, Xiong M, Xiao R, Xiong J, Zhang Q, Shao L
Received 19 August 2017
Accepted for publication 13 December 2017
Published 23 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1683—1695
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149012
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: ZWINT is a crucial component of the mitotic checkpoint. However,
its possible role in lung cancer is unclear. In this study, we determined its
correlation with lung cancer.
Methods: Real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to
determine 40 collected clinical lung cancer samples. Chi-square test was used
to examine possible correlations between ZWINT expression and
clinicopathological factors. The prognostic significance of mRNA expression of
ZWINT in lung cancer was evaluated using the Kaplan–Meier plotter. Univariate
and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis were performed to
determine whether ZWINT is an independent risk factor for overall survival (OS)
and disease-free survival (DFS) of lung cancer patients. Additionally, STRING
database was used to analyze protein-protein interactions.
Results: In this study, we screened 13 GSE datasets and detected that ZWINT is
highly expressed in multiple carcinomas including lung, melanoma, prostate,
nasopharyngeal, gastric, pancreatic, colon, esophageal, ovarian, renal, breast
and liver cancer. Real-time PCR and IHC results of collected clinical lung
cancer samples confirmed that ZWINT is highly expressed in tumor tissues
compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues. Additionally, high expression of ZWINT
might predict poor OS and DFS in lung cancer patients. Moreover, disease stage
and expression level of ZWINT were correlated with recurrence-free survival and
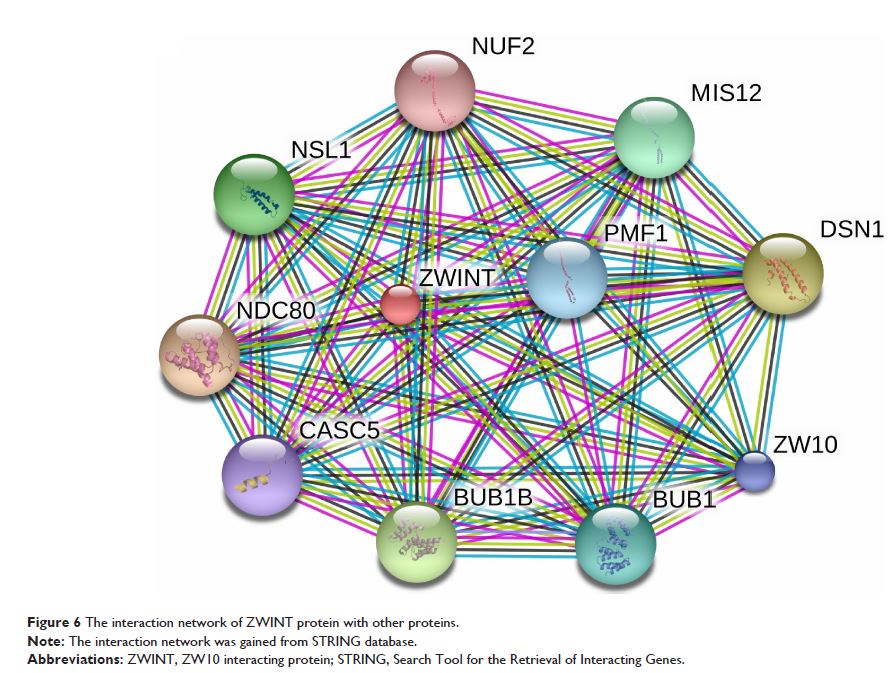
OS in lung cancer. Analysis of protein-protein interaction based on STRING
database gained 8 top genes which could interact with ZWINT, including PMF1 , MIS12 , DSN1 , ZW10 , BUB1 , BUB1B , CASC5 , NDC80 , NSL1 and NUF2 .
Conclusion: ZWINT is aberrantly highly expressed in lung tumor tissues and might be
involved in the pathogenesis of lung cancer.
Keywords: ZWINT, lung cancer, prognosis, overall survival, recurrence-free
survival