108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
新型非编码 RNA GACAT3 通过 miR-149 促进结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移
Authors Zhou W, Wang L, Miao Y, Xing R
Received 15 June 2017
Accepted for publication 20 November 2017
Published 19 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1543—1552
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S144103
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Manfred Beleut
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Aim: To explore the
expression and clinical significance of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) gastric
cancer-associated transcript 3 (GACAT3) in human colorectal cancer (CRC).
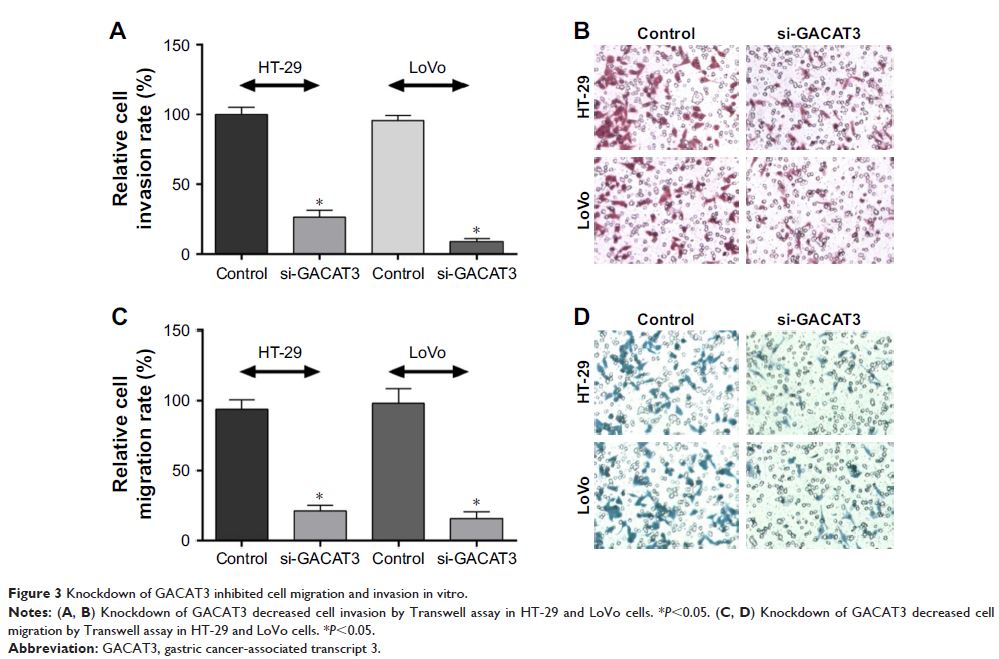
Methods: Expression of GACAT3 in CRC tissues and cell lines was measured using quantitative real-time PCR. CCK-8 and colony formation assays were used to assess the effect of GACAT3 on CRC cell line proliferation. Transwell invasion and migration assays were performed to detect the effect of GACAT3 on CRC cell line invasion and migration. Bioinformatics prediction, luciferase reporter assay, and pull-down assay were used to determine if miR-149 was a target of GACAT3. In addition, we also conducted colony formation assays and invasion assays to verify that GACAT3 promotes tumor progression through miR-149. Finally, in vivo tumorigenesis studies were used to demonstrate subcutaneous tumor growth.
Results: In the present study, we found that GACAT3 was highly expressed in CRC tissues and cell lines. Si-GACAT3 significantly decreased cell proliferation, motility, and invasiveness both in vitro and in vivo. We confirmed that downregulated GACAT3 significantly increased the expression of miR-149, and miR-149 binds to GACAT3 in a sequence-specific manner using luciferase reporter assays and pull-down assay. Further functional experiments indicated that GACAT3 could directly upregulate SP1 and STAT3 expressions by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-149, and consequentially, promoting CRC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that GACAT3 promotes tumor progression through competitive binding to miR-149 and suggests a promising new strategy for anti-CRC therapy.
Keywords: GACAT3, miR-149, colorectal cancer, growth, metastasis, SP1, STAT3
Methods: Expression of GACAT3 in CRC tissues and cell lines was measured using quantitative real-time PCR. CCK-8 and colony formation assays were used to assess the effect of GACAT3 on CRC cell line proliferation. Transwell invasion and migration assays were performed to detect the effect of GACAT3 on CRC cell line invasion and migration. Bioinformatics prediction, luciferase reporter assay, and pull-down assay were used to determine if miR-149 was a target of GACAT3. In addition, we also conducted colony formation assays and invasion assays to verify that GACAT3 promotes tumor progression through miR-149. Finally, in vivo tumorigenesis studies were used to demonstrate subcutaneous tumor growth.
Results: In the present study, we found that GACAT3 was highly expressed in CRC tissues and cell lines. Si-GACAT3 significantly decreased cell proliferation, motility, and invasiveness both in vitro and in vivo. We confirmed that downregulated GACAT3 significantly increased the expression of miR-149, and miR-149 binds to GACAT3 in a sequence-specific manner using luciferase reporter assays and pull-down assay. Further functional experiments indicated that GACAT3 could directly upregulate SP1 and STAT3 expressions by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-149, and consequentially, promoting CRC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that GACAT3 promotes tumor progression through competitive binding to miR-149 and suggests a promising new strategy for anti-CRC therapy.
Keywords: GACAT3, miR-149, colorectal cancer, growth, metastasis, SP1, STAT3