108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
聚合物纳米纤维基微芯片用于肺腺癌中循环肿瘤细胞的 EGFR 突变分析
Authors Jiang WT, Wang H, Cui YM, Lei YY, Wang YF, Xu D, Jiang N, Chen YS, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Cao J, Ke ZF
Received 17 November 2017
Accepted for publication 18 January 2018
Published 16 March 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1633—1642
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S157154
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Circulating tumor
cells (CTCs) detection, an approach considered to be “liquid biopsy”, is a
potential alternative method in clinical use for early diagnosis of solid tumor
progression.
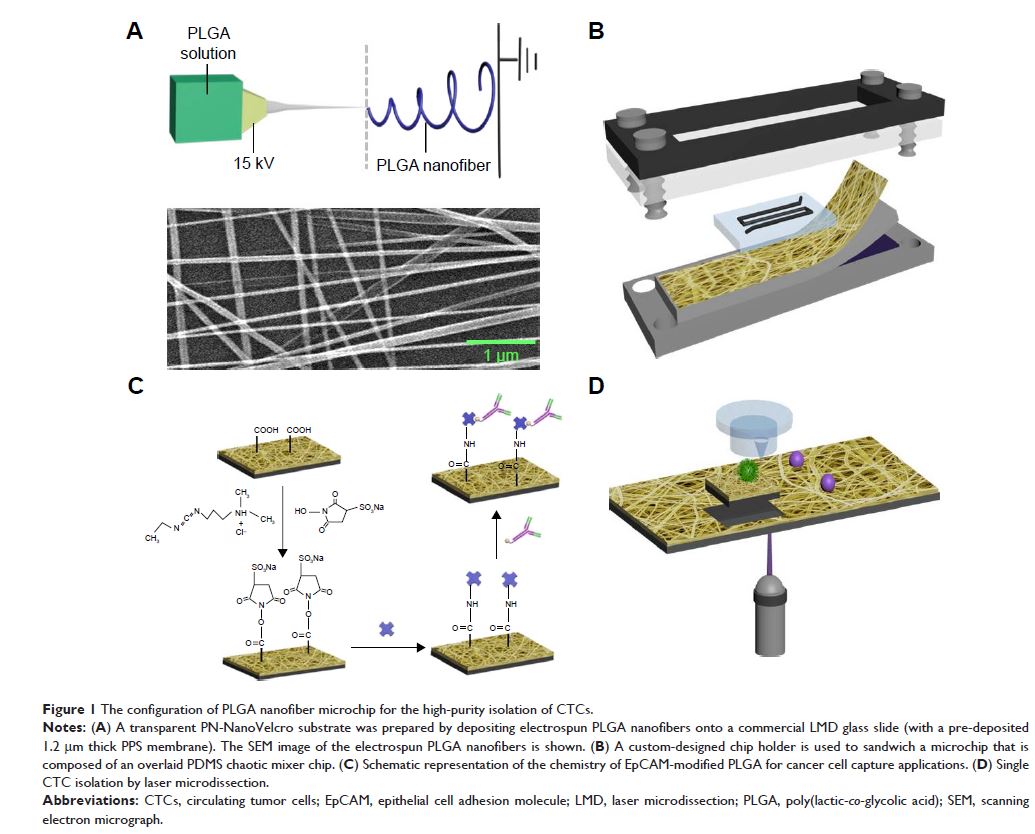
Methods: In this study, we developed a poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) – nanofiber (PN)-NanoVelcro chip as an efficient device for simple and rapid capture of CTCs from peripheral blood. We evaluated the device performance by assessing the capture efficiency and purity. Single CTC was isolated via laser microdissection system for subsequent genetic analysis, with an aim to find the concordance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations between tumor tissue and CTCs.
Results: PN-NanoVelcro chip exhibits great performance in capture efficiency and high purity. The genetic analysis results showed that most EGFR mutation in tumor tissue could also be detected in CTCs.
Conclusion: Compared to computed tomography image results, CTC detection can be implemented throughout the course of diseases and provides an accurate and earlier diagnosis of tumor progression, which make it possible for patients to acquire suitable and timely treatment.
Keywords: PN-NanoVelcro chip, CTCs, EGFR mutation, prognosis, lung adenocarcinoma
Methods: In this study, we developed a poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) – nanofiber (PN)-NanoVelcro chip as an efficient device for simple and rapid capture of CTCs from peripheral blood. We evaluated the device performance by assessing the capture efficiency and purity. Single CTC was isolated via laser microdissection system for subsequent genetic analysis, with an aim to find the concordance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations between tumor tissue and CTCs.
Results: PN-NanoVelcro chip exhibits great performance in capture efficiency and high purity. The genetic analysis results showed that most EGFR mutation in tumor tissue could also be detected in CTCs.
Conclusion: Compared to computed tomography image results, CTC detection can be implemented throughout the course of diseases and provides an accurate and earlier diagnosis of tumor progression, which make it possible for patients to acquire suitable and timely treatment.
Keywords: PN-NanoVelcro chip, CTCs, EGFR mutation, prognosis, lung adenocarcinoma