108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
miR-622 通过直接靶向 VEGFA 可抑制乳头状甲状腺癌的肿瘤形成
Authors Wang R, Ma Q, Ji L, Yao Y, Ma M, Wen Q
Received 12 November 2017
Accepted for publication 12 January 2018
Published 16 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1501—1509
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156810
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: MicroRNAs
(miRNAs) were reportedly to play crucial roles in papillary thyroid carcinoma
(PTC) tumorigenesis and development. Therefore, the discovery of miRNAs may
provide a new and powerful tool for diagnosis and treatment of PTC.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the biological function and underlying mechanism of miR-622 in PTC.
Materials and methods: The expression levels of miR-622 in PTC patient tissues and cell lines were determined by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). The biological function including cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion, as well as underling mechanism of miR-622 in PTC, were also evaluated by a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments.
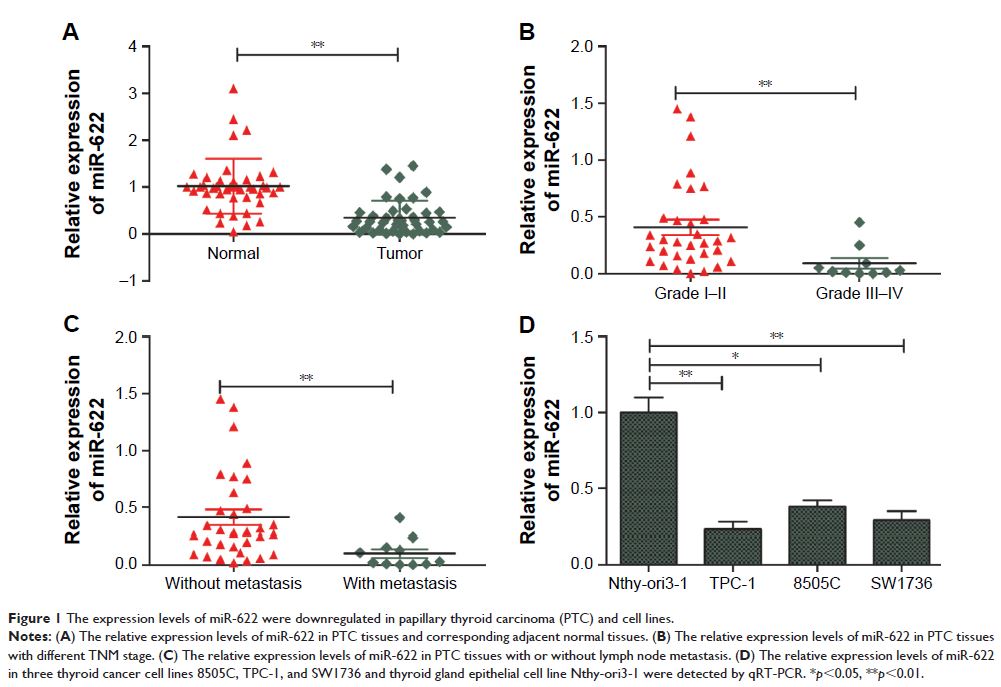
Results: miR-622 expression level was significantly downregulated in PTC tissues and cell lines. Decreased miR-622 expression was associated with advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis (P <0.01). The overexpression of miR-622 in TPC-1 cells inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, as well as suppress tumor growth in vivo. Moreover, we also demonstrated that miR-622 specifically targeted the 3'-UTR regions of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and inhibited its expression both mRNA level and protein levels. Overexpression of VEGFA reversed miR-622-mediated inhibition effect on cell proliferation, migration and invasion in thyroid cancer cells. More importantly, VEGFA expression was significantly increased and inversely correlated with the levels of miR-622 in PTC tissues.
Conclusion: These results show that miR-622 acts as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer, at least in part, via targeting VEGFA, and suggest that miR-622 may serves as a potential target for treatment of thyroid cancer patients.
Keywords: thyroid cancer, miR-622, VEGFA, proliferation, invasion
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the biological function and underlying mechanism of miR-622 in PTC.
Materials and methods: The expression levels of miR-622 in PTC patient tissues and cell lines were determined by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). The biological function including cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion, as well as underling mechanism of miR-622 in PTC, were also evaluated by a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Results: miR-622 expression level was significantly downregulated in PTC tissues and cell lines. Decreased miR-622 expression was associated with advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis (P <0.01). The overexpression of miR-622 in TPC-1 cells inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, as well as suppress tumor growth in vivo. Moreover, we also demonstrated that miR-622 specifically targeted the 3'-UTR regions of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and inhibited its expression both mRNA level and protein levels. Overexpression of VEGFA reversed miR-622-mediated inhibition effect on cell proliferation, migration and invasion in thyroid cancer cells. More importantly, VEGFA expression was significantly increased and inversely correlated with the levels of miR-622 in PTC tissues.
Conclusion: These results show that miR-622 acts as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer, at least in part, via targeting VEGFA, and suggest that miR-622 may serves as a potential target for treatment of thyroid cancer patients.
Keywords: thyroid cancer, miR-622, VEGFA, proliferation, invasion