108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
牡荆素通过 PI3K/Akt 信号通路途径保护 MPTP 诱导的帕金森病患者的多巴胺能神经元
Authors Hu M, Li F, Wang W
Received 13 November 2017
Accepted for publication 16 January 2018
Published 16 March 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 565—573
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S156920
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Abstract: Parkinson’s disease
(PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease which is characterized by the
degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta
(SNpc).
Methods: In this study, the neuroprotective effect of vitexin (Vit), a flavonoid compound isolated from Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge was examined in PD models both in vitro and in vivo.
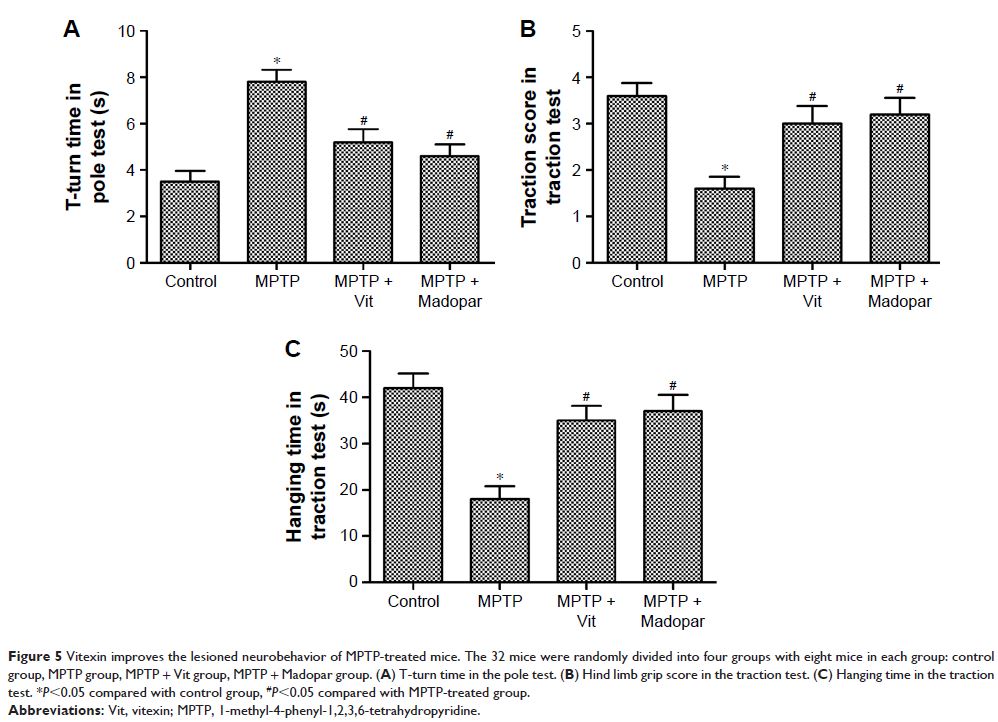
Results: On SH-SY5Y cells, methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) treatment suppressed cell viability, induced apoptosis, and increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. However, Vit improved these parameters induced by MPP+ treatment significantly. Further study disclosed that Vit enhanced the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt which was downregulated by MPP+ in SH-SY5Y cells, the effect of which could be blocked by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and activated by PI3K activator IGF-1. Moreover, results from the pole test and traction test suggested that Vit pretreatment prevented bradykinesia and alleviated the initial lesions caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in MPTP-treated mouse PD model. Vit also enhanced the activation of PI3K and Akt and suppressed the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 activity in MPTP-treated mice.
Conclusion: Taken together, this study demonstrated that Vit protected dopaminergic neurons against MPP+/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Our findings may facilitate the clinical application of Vit in the therapy of PD.
Keywords: vitexin, MPTP, Parkinson’s disease, PI3K/Akt, neuroprotective
Methods: In this study, the neuroprotective effect of vitexin (Vit), a flavonoid compound isolated from Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge was examined in PD models both in vitro and in vivo.
Results: On SH-SY5Y cells, methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) treatment suppressed cell viability, induced apoptosis, and increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. However, Vit improved these parameters induced by MPP+ treatment significantly. Further study disclosed that Vit enhanced the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt which was downregulated by MPP+ in SH-SY5Y cells, the effect of which could be blocked by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and activated by PI3K activator IGF-1. Moreover, results from the pole test and traction test suggested that Vit pretreatment prevented bradykinesia and alleviated the initial lesions caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in MPTP-treated mouse PD model. Vit also enhanced the activation of PI3K and Akt and suppressed the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 activity in MPTP-treated mice.
Conclusion: Taken together, this study demonstrated that Vit protected dopaminergic neurons against MPP+/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Our findings may facilitate the clinical application of Vit in the therapy of PD.
Keywords: vitexin, MPTP, Parkinson’s disease, PI3K/Akt, neuroprotective