108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Rhein 通过影响 MAPK/NF-κB 信号通路抑制人肾癌细胞恶性表型
Authors Ma YL, Chen F, Shi J
Received 11 October 2017
Accepted for publication 17 January 2018
Published 14 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1385—1394
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S153798
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Rhein,
an anthraquinone derivative of rhubarb, is traditionally used in Chinese herbal
medicine. Now emerging studies suggest its antitumor properties in many human
cancers. The present study aims to investigate the antitumor role of Rhein and
its possible mechanism in human renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Materials and
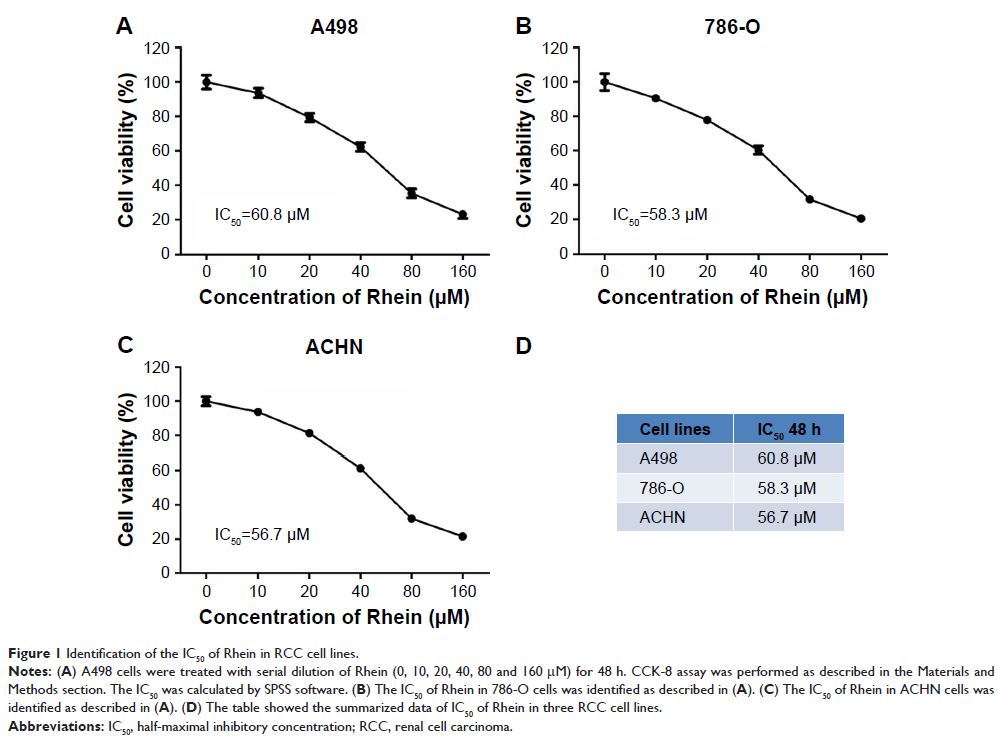
methods: Three RCC cell lines (A489,
786-O and ACHN) were used as the cell models. We applied CCK-8, cell counting,
colony formation, wound healing and Transwell assays to assess the antitumor
roles of Rhein in RCC cells in vitro. The therapeutic efficacy of Rhein was
further evaluated by intraperitoneal administrations in tumor formation of
mice. Western blot was used to investigate the underlying mechanisms of action
of Rhein.
Results: Rhein inhibited RCC cell proliferation in a dose- and time-dependent
manner. It also suppressed RCC cell migration and invasion in vitro. Moreover,
Rhein was able to inhibit tumor growth in nude mice by intraperitoneal
administration in vivo. Mechanistically, the protein levels of phosphorylated
MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase
and c-Jun N-terminal kinase), phosphorylated Akt and two targets of NF-κB
(nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells) pathway,
matrix metalloproteinase 9 and CCND1 were all markedly reduced by Rhein
treatment.
Conclusion: Rhein processed the antitumor effects in RCC cells by inhibiting
cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and these tumor-suppressing
functions might be mediated by MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Keywords: Rhein, renal cell carcinoma, antitumor effects, MAPK, NF-κB