108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有肿瘤特异性和 pH 响应性的肽修饰下含脂质体的紫杉醇的治疗诊断学效率与超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒
Authors Zheng XC, Ren W, Zhang S, Zhong T, Duan XC, Yin YF, Xu MQ, Hao YL, Li ZT, Li H, Liu M, Li ZY, Zhang X
Received 15 November 2017
Accepted for publication 25 January 2018
Published 13 March 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1495—1504
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S157082
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
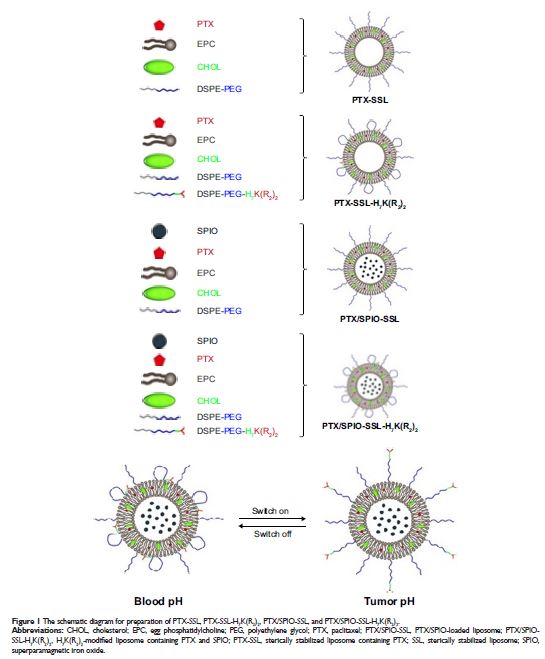
Background: In
the present study, the tumor-specific, pH-responsive peptide H7K(R2)2 -modified, theranostic liposome-containing paclitaxel (PTX) and
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIO NPs), PTX/SPIO-SSL-H7K(R2)2, was prepared by using H7K(R2)2 as the targeting ligand, SPIO NPs as the magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI) agent, PTX as antitumor drug.
Methods: The PTX/SPIO-SSL-H7K(R2)2 was prepared by a thin film hydration method. The characteristics of
PTX/SPIO-SSL-H7K(R2)2 were evaluated.
The targeting effect, MRI, and antitumor activity of PTX/SPIO-SSL-H7K(R2)2 were investigated detail in vitro and in vivo in human breast
carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cell models.
Results: Our results of in vitro flow cytometry, in vivo imaging, and in
vivo MR imaging confirmed the pH-responsive characteristic of H7K(R2)2 in MDA-MB-231 cell line in vitro and in vivo. The results of
in vivo MRI and in vivo antitumor activity confirmed the theranostic effect of
PTX/SPIO-SSL-H7K(R2)2 in MDA-MB-231
tumor-bearing model.
Conclusion: Considering all our in vitro and in vivo results, we conclude that
we developed targeting modified theranostic liposome which could achieve both
role of antitumor and MRI.
Keywords: tumor-specific pH-responsive peptide, paclitaxel,
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, liposome, theranostic efficiency