108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

p-STAT3 在肝细胞癌患者中的临床病理学意义和预后作用
Authors Liang CJ, Xu Y, Ge H, Li G, Wu J
Received 6 November 2017
Accepted for publication 26 January 2018
Published 5 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1203—1214
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156198
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background and aim: Constitutive activation of STAT3 through its phosphorylation
(p-STAT3) plays a key role in the development and progression of various
cancers. However, the relationship between p-STAT3 expression and the
clinicopathological features and prognostic value in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains controversial. We conducted a
meta-analysis to evaluate the role of p-STAT3 in HCC.
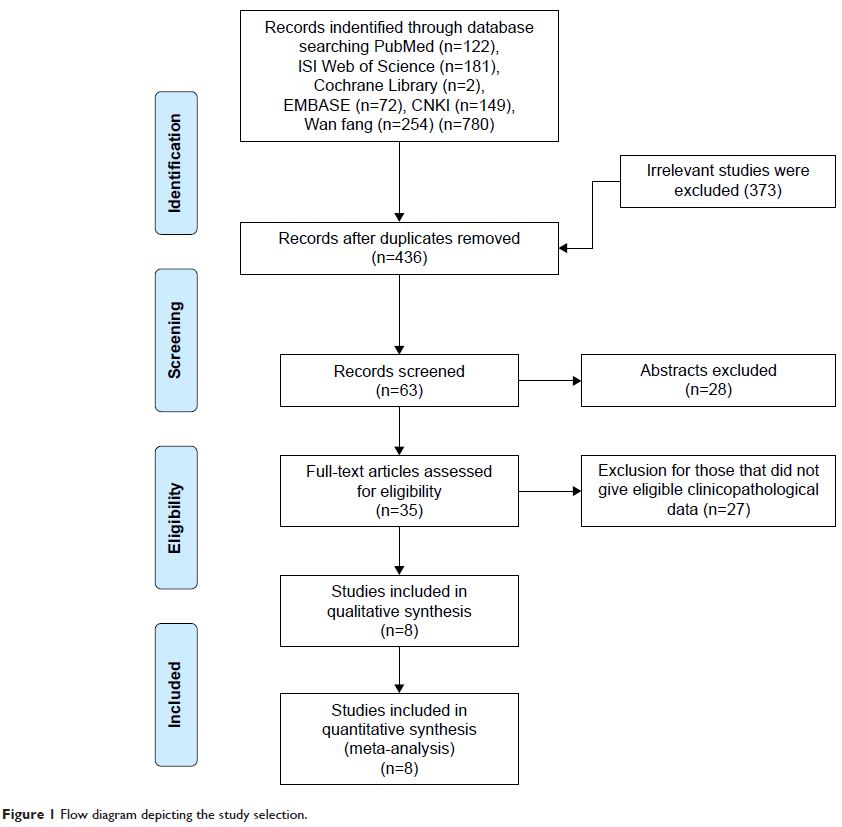
Methods: The PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, EMBASE, Chinese
CNKI, and Chinese Wanfang databases were searched using the appropriate terms
to find the relevant studies on p-STAT3 and HCC. The relationship between
p-STAT3 expression and clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic value
was established. Pool odds ratios (ORs) and hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs
were calculated using the STATA 14.2 software.
Results: The eight articles included in this meta-analysis comprised 752
patients. Expression of p-STAT3 was associated with incidence, age, liver
cirrhosis, tumor size, vascular invasion, and TNM stage of HCC, but it was not
related to gender, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), hepatitis B surface antigen
(HBsAg), number of tumors, and tumor differentiation. Additionally, the
expression of p-STAT3 was related to a poor 3- and 5-year overall survival rate
and disease-free survival rate.
Conclusion: Expression of p-STAT3 was associated with the incidence, age,
liver cirrhosis, tumor size, vascular invasion, and TNM stage. Thus, p-STAT3
can be a reliable prognostic biomarker for HCC. Further high-quality studies
with larger numbers of patients are needed.
Keywords: p-STAT3, hepatocellular carcinoma, prognosis, meta-analysis