108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
吴茱萸碱通过在胶质瘤中抑制 PI3K/AKT 和激活 MAPK 来促进细胞凋亡
Authors Wang R, Deng D, Shao N, Xu Y, Xue L, Peng Y, Liu Y, Zhi F
Received 26 October 2017
Accepted for publication 18 January 2018
Published 2 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1183—1192
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155275
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Background: Glioblastoma
multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant primary tumor of the central nervous
system and is associated with a very poor prognosis. No further improvements in
outcomes have been reported since radiotherapy-temozolomide therapy was
introduced. Therefore, developing new agents to treat GBM is important.
Aim: This study aimed to evaluate the anti-tumor effect of evodiamine (Evo) on GBM cells, and to determine the underlying mechanisms involved.
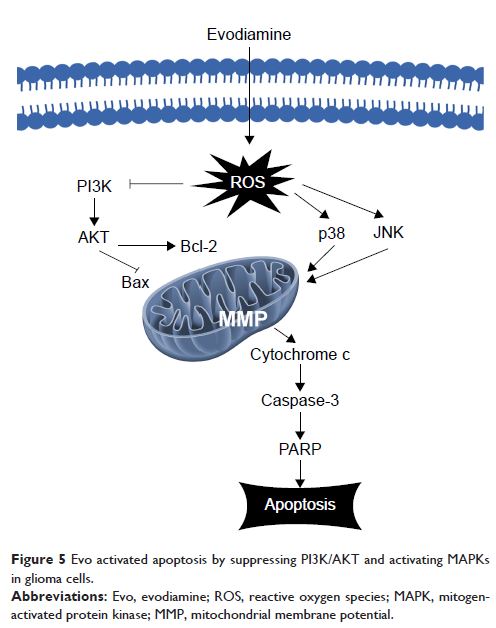
Results: According to MTT assay results, Evo significantly inhibited the cell proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry analyses revealed that Evo induced cell apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, Evo induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) disruption. Finally, Evo induced apoptosis in cancer cells by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling and inducing MAPK phosphorylation (p38 and JNK, but not ERK) to regulate apoptotic proteins (Bax, Bcl-2, Cytochrome c, Caspase-3, and PARP).
Conclusion: In summary, Evo inhibits cell proliferation by inducing cellular apoptosis via suppressing PI3K/AKT and activating MAPK in GBM; these results indicate that Evo may be regarded as a new approach for GBM treatment.
Keywords: evodiamine, apoptosis, Akt, MAPK, glioma
Aim: This study aimed to evaluate the anti-tumor effect of evodiamine (Evo) on GBM cells, and to determine the underlying mechanisms involved.
Results: According to MTT assay results, Evo significantly inhibited the cell proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry analyses revealed that Evo induced cell apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, Evo induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) disruption. Finally, Evo induced apoptosis in cancer cells by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling and inducing MAPK phosphorylation (p38 and JNK, but not ERK) to regulate apoptotic proteins (Bax, Bcl-2, Cytochrome c, Caspase-3, and PARP).
Conclusion: In summary, Evo inhibits cell proliferation by inducing cellular apoptosis via suppressing PI3K/AKT and activating MAPK in GBM; these results indicate that Evo may be regarded as a new approach for GBM treatment.
Keywords: evodiamine, apoptosis, Akt, MAPK, glioma