108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FOXA2 和 SIRT6 的协同作用通过 ZEB2 抑制减缓肝细胞癌的发展
Authors Liu J, Yu Z, Xiao Y, Meng Q, Wang Y, Chang W
Received 1 September 2017
Accepted for publication 27 November 2017
Published 1 March 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 391—402
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S150552
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: The Forkhead transcription
family member FOXA2 plays a fundamental role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
progression, but the precise interaction factor and molecular regulation of
FOXA2 are not fully understood.
Objective: In this study, we found that FOXA2 could
interact with sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) directly in vivo and in vitro. We explored that
the expressions of FOXA2 and SIRT6 were significantly downregulated in human
HCC and HCC cell lines.
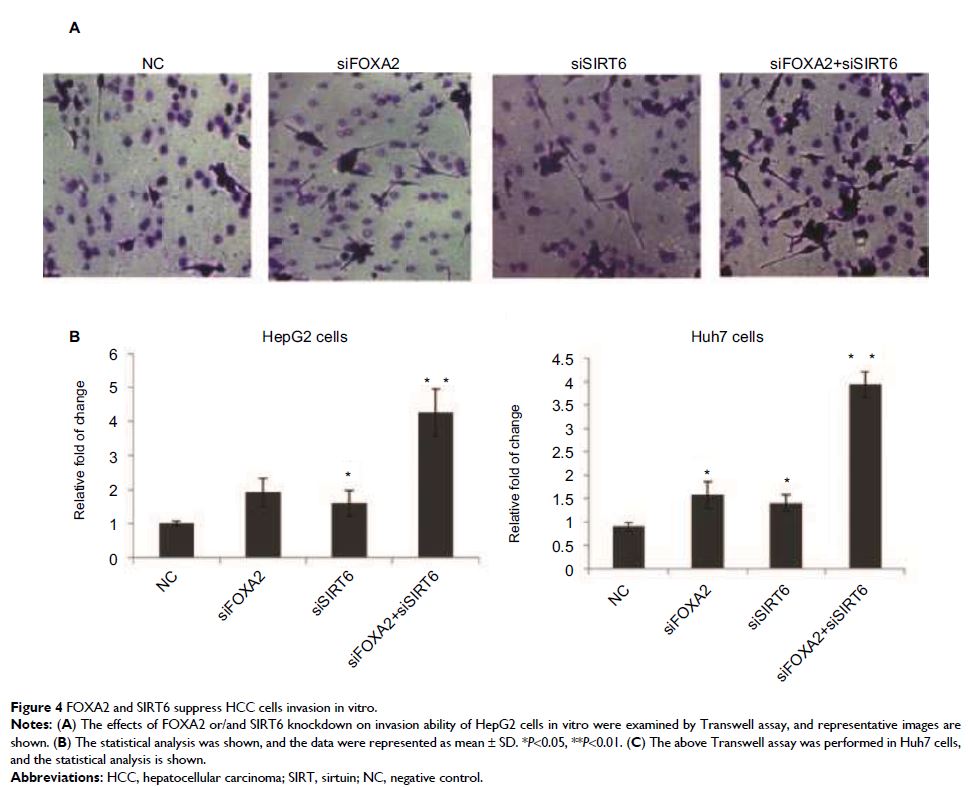
Methods: Functionally, cell counting kit-8 assay and
Transwell® assay were performed; we demonstrated that the knockdown of FOXA2
and SIRT6 promoted HepG2 cells and Huh7 cells proliferation and invasion in
vitro.
Results: Mechanically, using luciferase reporter assay and fast
chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, we showed that FOXA2 and SIRT6 regulated
the expression of ZEB2 from transcription level. ZEB2 suppression was involved
in the anti-oncogenesis effect of FOXA2 and SIRT6. The negative correlation
between the expressions of ZEB2 and FOXA2 or SIRT6 was observed in the tissues
of HCC patients.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that the coordination
function of FOXA2 and SIRT6 played a critical role in HCC progression and may
serve as potential drug candidates for HCC.
Keywords: FOXA2, SIRT6,
ZEB2, proliferation, invasion