108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

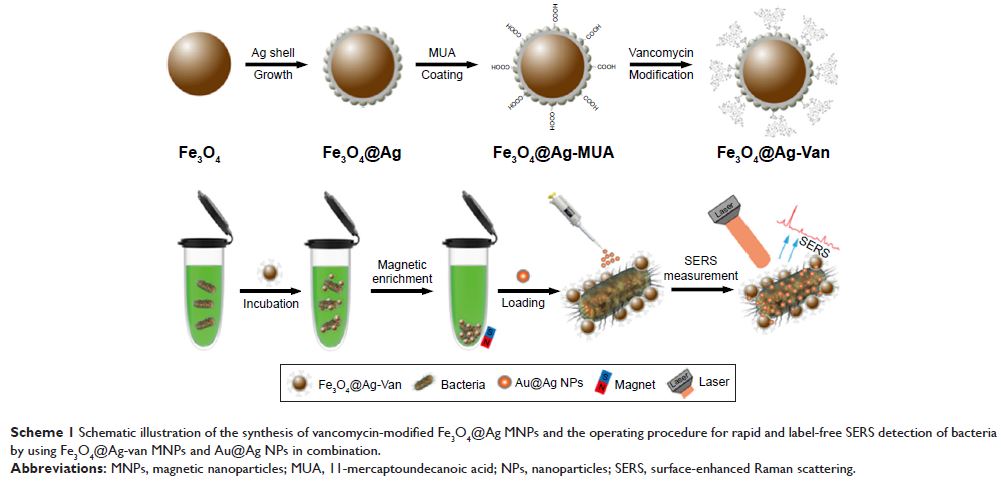
万古霉素修饰的 Ag 包被的磁性纳米颗粒和二级增强纳米颗粒联合使用以快速表面增强拉曼散射检测细菌
Authors Wang CW, Gu B, Liu QQ, Pang YF, Xiao R, Wang SQ
Received 30 August 2017
Accepted for publication 7 December 2017
Published 27 February 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1159—1178
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S150336
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Pathogenic bacteria have always been a significant threat to human
health. The detection of pathogens needs to be rapid, accurate, and convenient.
Methods: We present a sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)
biosensor based on the combination of vancomycin-modified Ag-coated magnetic
nanoparticles (Fe3O4@Ag-Van MNPs) and Au@Ag
nanoparticles (NPs) that can effectively capture and discriminate bacterial
pathogens from solution. The high-performance Fe3O4@Ag MNPs were modified
with vancomycin and used as bacteria capturer for magnetic separation and
enrichment. The modified MNPS were found to exhibit strong affinity with a
broad range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. After separating and
rinsing bacteria, Fe3O4@Ag-Van MNPs and Au@Ag
NPs were synergistically used to construct a very large number of hot spots on
bacteria cells, leading to ultrasensitive SERS detection.
Results: The dominant merits of our dual enhanced strategy included high
bacterial-capture efficiency (>65%) within a wide pH range (pH 3.0–11.0), a
short assay time (<30 min), and a low detection limit (5×102 cells/mL). Moreover, the spiked tests show that this method is
still valid in milk and blood samples. Owing to these capabilities, the
combined system enabled the sensitive and specific discrimination of different
pathogens in complex solution, as verified by its detection of Gram-positive
bacterium Escherichia coli , Gram-positive
bacterium Staphylococcus aureus , and
methicillin-resistant S. aureus .
Conclusion: This method has great potential for field applications in food
safety, environmental monitoring, and infectious disease diagnosis.
Keywords: surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Fe3O4@Ag magnetic
nanoparticle, Au@Ag nanoparticles, vancomycin-modified, rapid bacteria
detection