108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Reversine(取代嘌呤)通过诱导细胞凋亡和多倍体对人肾癌细胞产生抑制作用
Authors Cheng L, Wang H, Guo KC, Wang ZC, Zhang ZY, Shen C, Chen L, Lin J
Received 27 November 2017
Accepted for publication 17 January 2018
Published 26 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1025—1035
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S158198
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Human renal cell
carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer that arises from the
renal epithelium. Up to 33.3% of RCC patients treated with local tumor
resections will subsequently develop recurrence or metastases. Thus, optimized
therapeutic regimes are urgently needed to improve the prognosis of RCC.
Reversine was recently reported to exert critical roles in cancer therapy.
Materials and methods: This study evaluated the anti-tumor effects of
reversine on cell viability, colony formation, apoptosis, and cell cycle in
786-O and ACHN cell lines.
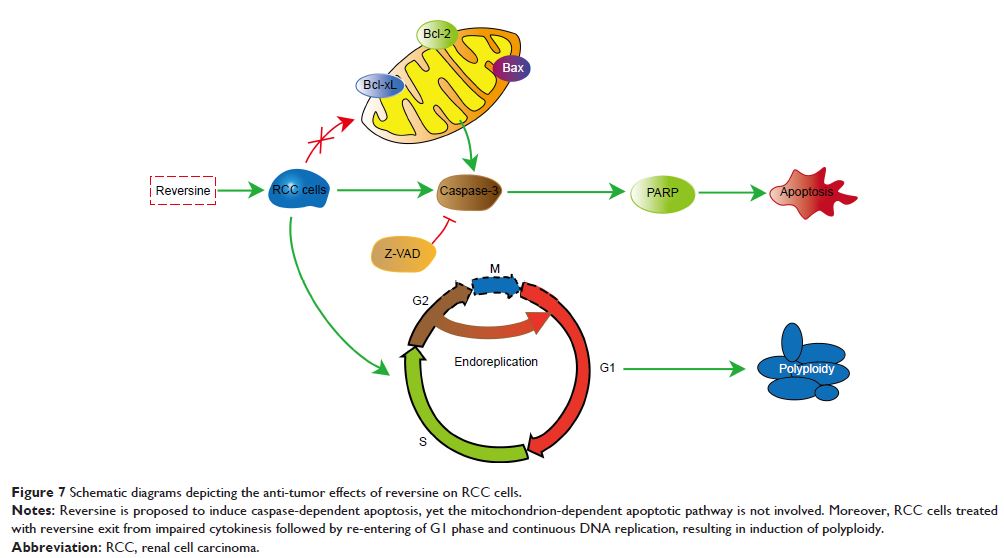
Results: It was demonstrated that reversine significantly
inhibited the proliferation of both cell lines in time- and dose-dependent
manners. Polyploidy formation was observed under high-concentration reversine
treatment. In addition, reversine induced cell death via caspase-dependent
apoptotic pathways, which could be partially inhibited by Z-VAD-FMK, a
pan-caspase inhibitor.
Conclusion: Reversine could effectively suppress the
proliferation of human RCC cells, and may serve as a novel therapeutic regimen
for RCC in clinical practice.
Keywords: anti-cancer,
apoptosis, Aurora kinase, human renal cell carcinoma, polyploidy, reversine