109814
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
采用巯基丁二酸涂层近红外量子点的被动肿瘤靶向和成像
Authors Lin G, Wang X, Yin F, Yong KT
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 335—345
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S74805
Received 23 September 2014, Accepted 22 November 2014, Published 6 January 2015
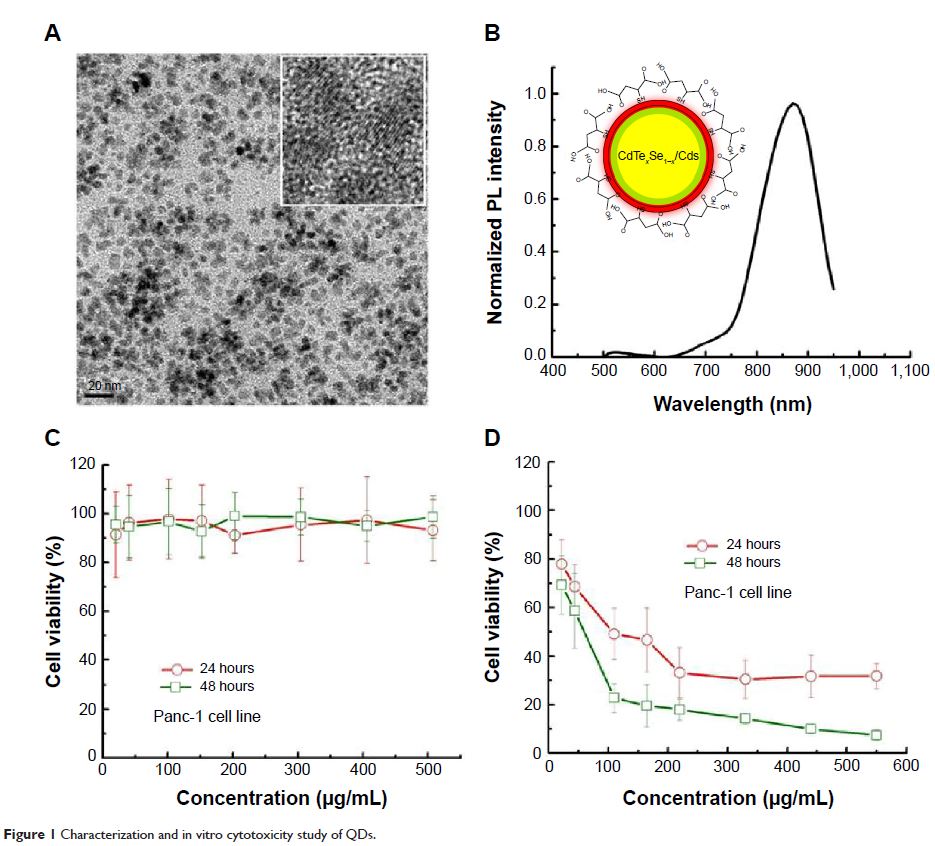
Abstract: In this paper, we demonstrate the preparation of monodispersed quantum
dots (QDs) as near-infrared (NIR) optical probes for in vivo pancreatic cancer
targeting and imaging. The design of these luminescent probes involves
functionalizing NIR QDs with ligand mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA), which targets
the tumor site by enhanced permeability and retention effect. The colloidal and
optical stability of the QDs can be maintained for >1 week. In vivo
optical imaging studies in nude mice bearing pancreatic tumor show that the
probes accumulate at tumor sites for >2.5 hours following intravenous
injection of the functionalized NIR QDs. Tumor-labeling studies showed no
evidence of harmful effects on the treated animals, even at a dose as high as
~50 mg/kg. These results demonstrate that the engineered
MSA-functionalized QDs can serve as a diagnostic platform for early detection
of cancer, as well as in image-guided precise surgical resection of tumors.
Keywords: QDs, near-infrared, mercaptosuccinic acid, pancreatic cancer, tumor targeting
Keywords: QDs, near-infrared, mercaptosuccinic acid, pancreatic cancer, tumor targeting