108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

术中右美托咪定可减轻经皮肾镜取石术患者术后的全身炎症反应综合征:一个回顾性队列研究
Authors Tan F, Gan X, Deng Y, Li X, Guo N, Hei Z, Zhu Q, Chen ZG, Zhou S
Received 17 November 2017
Accepted for publication 22 December 2017
Published 14 February 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 287—293
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S157320
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Purpose: Dexmedetomidine (DEX) has been reported to attenuate inflammation in
rats. The present retrospective cohort study aimed to investigate whether
intraoperative administration with DEX could reduce the incidence of
postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in patients
following percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL).
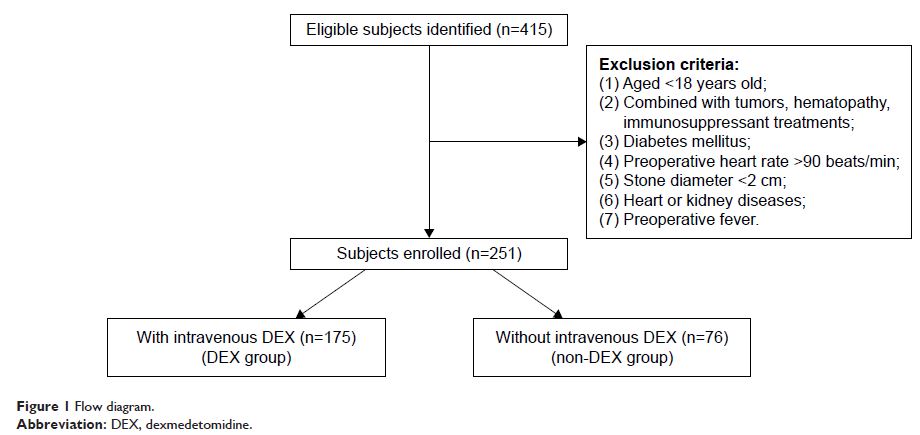
Patients and methods: A
total of 251 patients were included in the analysis. Among these patients, 175
received intravenous DEX infusion during the intraoperative period and 76 did
not. The primary outcome measures were the incidences of postoperative SIRS and
fever. Secondary outcomes included patient-controlled analgesia (tramadol)
requirements, length of postoperative hospitalization stay, serum creatinine
(Scr) and serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) concentration, and adverse events
(bradycardia, hypotension, renal artery thrombosis).
Results: Administration
of DEX not only significantly attenuated the incidence of SIRS and fever (P =0.029, P =0.042, respectively), but also
reduced analgesia requirements (P =0.028). The
length of postoperative hospitalization stay, Scr and BUN concentration, and
adverse events did not differ significantly between the two groups. Further
univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that
intraoperative DEX administration was a protective factor against SIRS after
PCNL (OR 0.476 [95% CI: 0.257–0.835]; P =0.019).
Conclusion: Intraoperative
administration of DEX might be associated with reductions in the incidences of
SIRS and fever after PCNL.
Keywords: PCNL, SIRS,
risk factor, dexmedetomidine