108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有壳聚糖 - 谷胱甘肽 - 甘氨酰肌氨酸和层状双氢氧化物的功能性嵌入纳米复合物用于局部眼用药物递送
Authors Xu T, Xu X, Gu Y, Fang L, Cao F
Received 2 August 2017
Accepted for publication 9 December 2017
Published 13 February 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 917—937
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S148104
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: To enhance ocular bioavailability, the traditional strategies have
focused on prolonging precorneal retention and improving corneal permeability
by nano-carriers with positive charge, thiolated polymer, absorption enhancer
and so on. Glycylsarcosine (GS) as an active target ligand of the peptide
tranpsporter-1 (PepT-1), could specific interact with the PepT-1 on the cornea
and guide the nanoparticles to the treating site.
Purpose: The objective of the study was to explore the active targeting
intercalated nanocomposites based on chitosan-glutathione-glycylsarcosine
(CG-GS) and layered double hydroxides (LDH) as novel carriers for the treatment
of mid-posterior diseases.
Materials and
methods: CG-GS-LDH intercalated
nanocomposites were prepared by the coprecipitation hydrothermal method. In
vivo precorneal retention study, ex vivo fluorescence images, in vivo
experiment for distribution and irritation were studied in rabbits. The
cytotoxicity and cellular uptake were studied in human corneal epithelial
primary cells (HCEpiC).
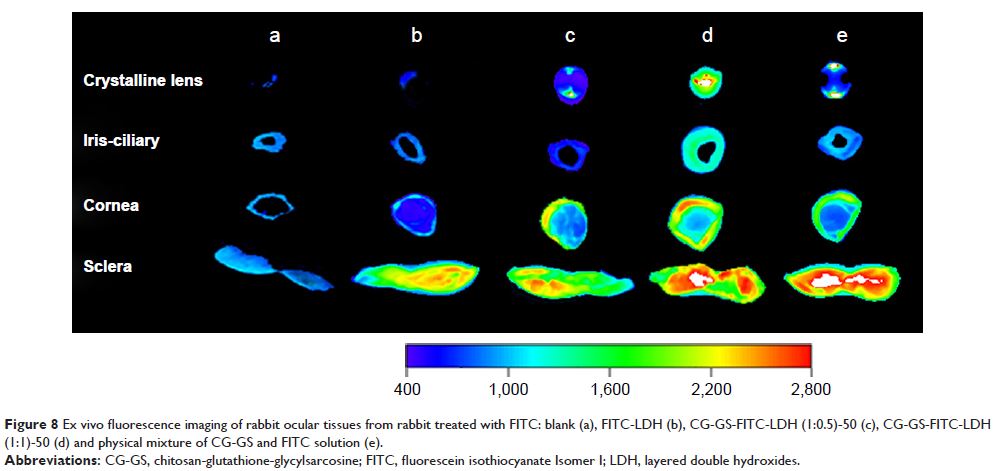
Results: CG-GS-LDH nanocomposites were prepared successfully and
characterized by FTIR and XRD. Experiments with rabbits showed longer
precorneal retention and higher distribution of fluorescence probe/model drug.
In vitro cytological study, CG-GS-LDH nanocomposites exhibited enhanced
cellular uptake compared to pure drug solution. Furthermore, the investigation
of cellular uptake mechanisms demonstrated that both the active transport by
PepT-1 and clathrin-mediated endocytosis were involved in the internalization
of CG-GS-LDH intercalated nanocomposites. An ocular irritation study and a
cytotoxicity test indicated that these nanocomposites produced no significant
irritant effects.
Conclusions: The active targeting intercalated nanocomposites could have great
potential for topical ocular drug delivery due to the capacity for prolonging
the retention on the ocular surface, enhancing the drug permeability through
the cornea, and efficiently delivering the drug to the targeted site.
Keywords: active targeting, intercalated nanocomposites, peptide
transporter-1, layered double hydroxides, glycylsarcosine