108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MRSA 对 CYP450 的影响:MRSA 感染小鼠细菌因子、氧化应激和药物代谢酶的动态变化
Authors Tang HQ, Long NN, Lin L, Liu Y, Li JL, Sun FH, Guo LJ, Zhang F, Dai M
Received 12 October 2017
Accepted for publication 27 November 2017
Published 13 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 229—238
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S153871
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
is a very damaging and widespread pathogen, which is associated with many
diseases and causes serious infections. MRSA infection can modulate the effects
of drugs, which may occur through an influence on cytochrome P450 (CYP450), the
drug-metabolizing enzyme in the liver. In this study, we evaluated the
underlying mechanism of drug failure or poisoning in MRSA infection.
Materials and
methods: Mice were infected with three
different doses of MRSA and the changes in CYP450 expression, cytokines, and
oxidative stress markers were evaluated.
Results: The administration of an attack dose of MRSA caused serious
symptoms of infection and resulted in a 40% mortality rate in the mice. MRSA
induced strong inflammation and oxidative stress in the mice, predominantly caused
by significant increases in interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-4, IL-6, macrophage
inflammatory protein, glutathione S-transferase
(GST), and malondialdehyde, and decreases in oxygen radical absorbance capacity
and glutathione levels in the liver. The expression of IL-2, tumor necrosis
factor-α, and GST was briefly suppressed, but increased on days 3 and 7. The
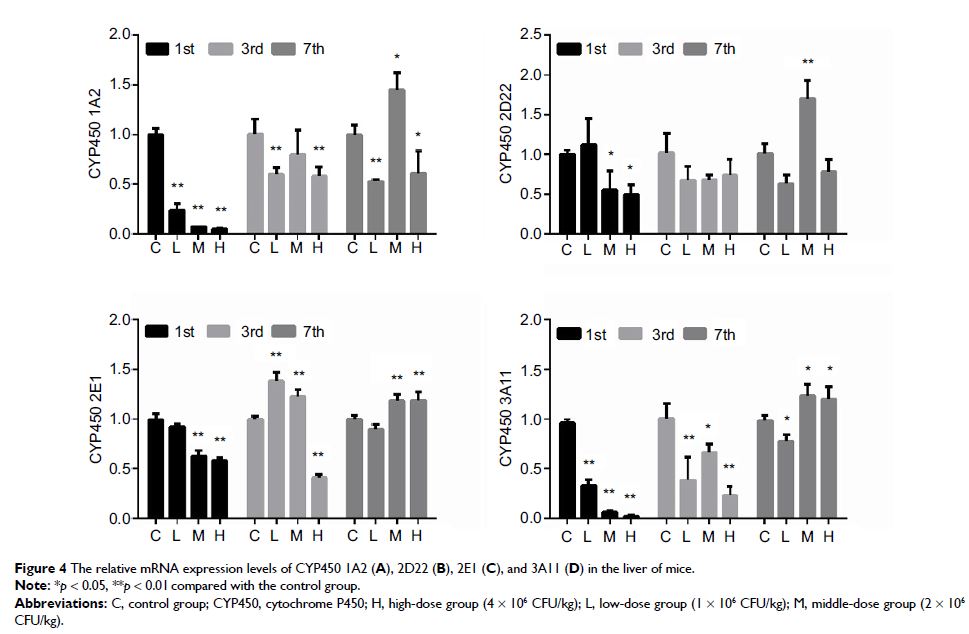
increased inflammation and oxidative stress further induced a significant
decrease in the mRNA levels and activities of CYP450 1A2, 2D22, 2E1, and 3A1 in
MRSA-infected mice within the first day of infection.
Conclusion: These results show that MRSA infection leads to inflammation and
oxidative stress, and reduces the expression levels and activities of drug
metabolism enzymes, which decreased drug metabolism in patients infected with
MRSA. Therefore, to avoid a drug overdose, the plasma concentration of patients
with MRSA infection should be continuously monitored.
Keywords: MRSA, infection, cytokines, oxidative stress, CYP450