108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Nemo 样激酶在宫颈鳞癌中的表达:一项临床病理学研究
Authors Yang W, Gu L, Yang C, Liu T
Received 15 October 2017
Accepted for publication 13 December 2017
Published 8 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 743—749
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154188
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Objective: Nemo-like
kinase (NLK) has been reported to play different roles in tumors. However, the
role of NLK in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) remains unknown. In this
study, we explored the clinical significance including survival of NLK protein
expression in CSCCs.
Patients and
methods: Immunohistochemical method was
performed using tissues from 130 patients with CSCC. The associations
between NLK expression and the clinicopathological factors and prognosis of
CSCCs were evaluated. Statistical analyses were performed using the chi-square
test, the multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, and the Kaplan–Meier
method.
Results: Immunohistochemical staining analysis showed that NLK was localized
predominately in the nucleus of the tumor cells, and increased NLK expression
was detected in 71 (54.6%) of 130 patients. NLK overexpression significantly
correlated with higher histological grade (P =0.001),
vascular/lymphatic invasion (P =0.010), lymph
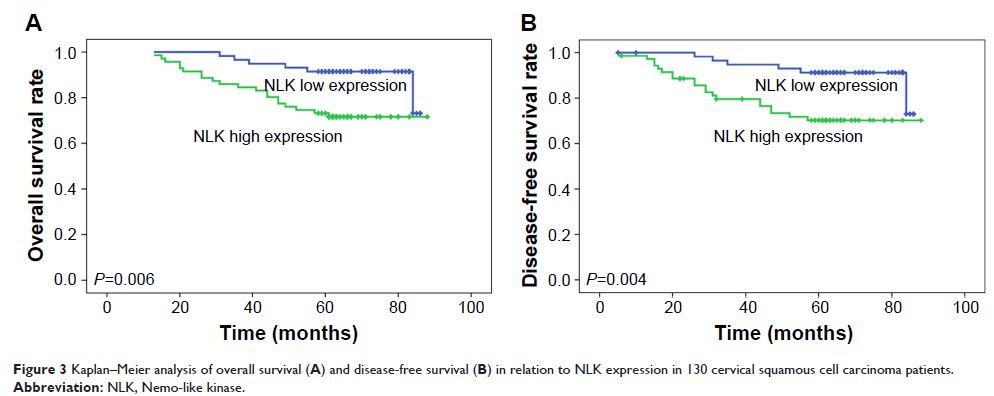
node metastasis (P =0.012), and recurrence (P =0.022). Patients with elevated
NLK expression had poorer overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS)
(P =0.006 and P =0.004, respectively) compared
with patients with decreased NLK expression. Multivariate Cox analysis
demonstrated that NLK overexpression was an independent factor for OS and DFS (P =0.034 and P =0.025, respectively).
Conclusion: NLK may be a valuable biomarker for predicting the prognosis of
CSCC patients and may serve as a potential target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Nemo-like kinase, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis,
progression, lymph node metastasis, survival, biomarker