108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载 BMP2 相关肽的矿化 ECM/肝素复合支架诱导骨再生
Authors Sun TF, Liu M, Yao S, Ji YH, Shi L, Tang K, Xiong ZK, Yang F, Chen KF, Guo XD
Received 27 September 2017
Accepted for publication 7 December 2017
Published 5 February 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 791—804
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S152698
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: At present, the treatment of osteoporotic defects poses a great
challenge to clinicians, owing to the lower regeneration capacity of the
osteoporotic bone as compared with the normal bone. The guided bone
regeneration (GBR) technology provides a promising strategy to cure
osteoporotic defects using bioactive membranes. The decellularized matrix from
the small intestinal submucosa (SIS) has gained popularity for its natural
microenvironment, which induces cell response.
Materials and
methods: In this study, we developed
heparinized mineralized SIS loaded with bone morphogenetic protein 2
(BMP2)-related peptide P28 (mSIS/P28) as a novel GBR membrane for guided
osteoporotic bone regeneration. These mSIS/P28 membranes were obtained through
the mineralization of SIS (mSIS), followed by P28 loading onto heparinized mSIS.
The heparinized mSIS membrane was designed to improve the immobilization
efficacy and facilitate controlled release of P28. P28 release from
mSIS-heparin-P28 and its effects on the proliferation, viability, and
osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal stem cells from
ovariectomized rats (rBMSCs-OVX) were investigated in vitro. Furthermore, a
critical-sized OVX calvarial defect model was used to assess the bone
regeneration capability of mSIS-heparin-P28 in vivo.
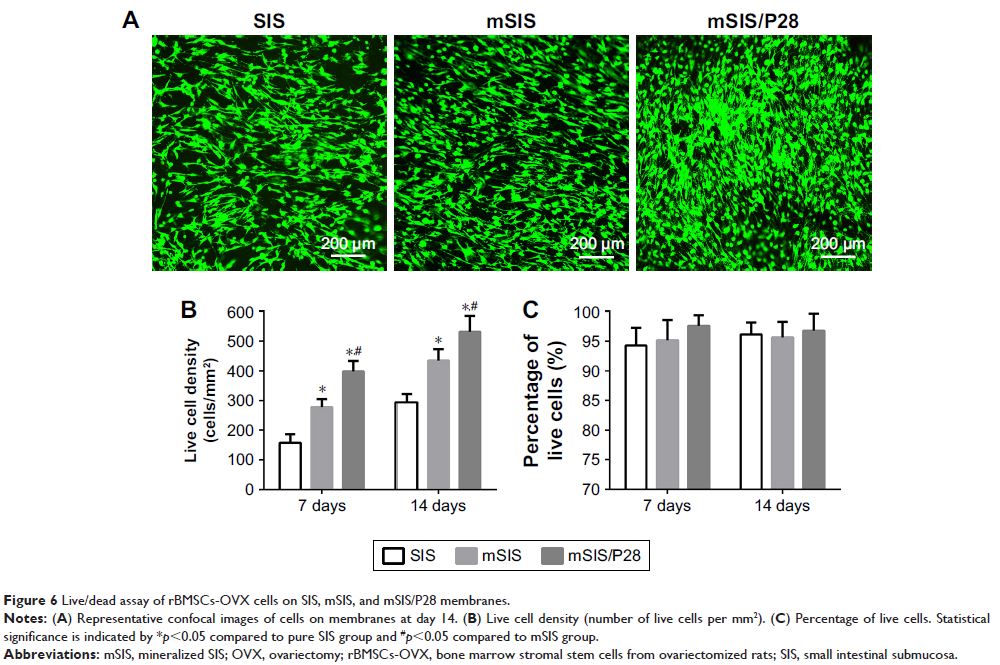
Results: In vitro results showed that P28 release from mSIS-heparin-P28
occurred in a controlled manner, with a long-term release time of 40 days.
Moreover, mSIS-heparin-P28 promoted cell proliferation and viability, alkaline
phosphatase activity, and mRNA expression of osteogenesis-related genes in
rBMSCs-OVX without the addition of extra osteogenic components. In vivo
experiments revealed that mSIS-heparin-P28 dramatically stimulated osteoporotic
bone regeneration.
Conclusion: The heparinized mSIS loaded with P28 may serve as a potential GBR
membrane for repairing osteoporotic defects.
Keywords: osteoporotic defect, guided bone regeneration, decellularized
matrix, heparin, BMP2-related peptide, control release