108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

APC 高甲基化在食管癌中的早期诊断潜力
Authors Wang B, Song H, Jiang H, Fu Y, Ding X, Zhou C
Received 9 August 2017
Accepted for publication 27 November 2017
Published 1 February 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 181—198
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S148677
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Luzhe Sun
Background: The hypermethylation of
APC gene is observed in various cancers, including esophageal cancer (EC).
However, the association between APC methylation and the initiation and
progression of EC is poorly understood.
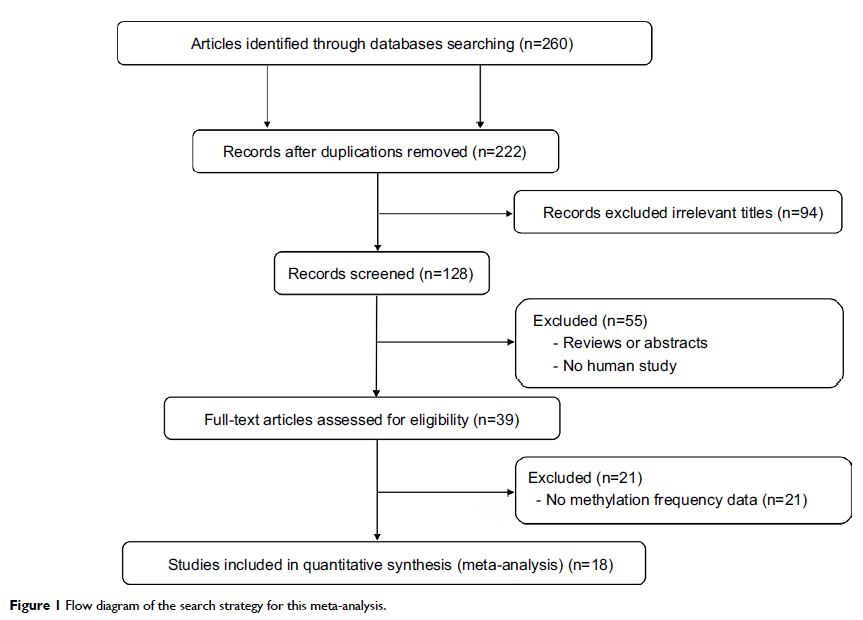
Purpose and methods: The current study systematically reviewed studies on
abnormal methylation of APC in EC and quantitatively synthesized 18 studies by
meta-analysis involving 1008 ECs, 570 Barrett’s esophagus (BE), and 782
controls.
Results: Our results showed higher methylation of APC in EC (OR
= 23.33, P < 0.001) and BE (OR =
9.34, P < 0.001) than in normal controls.
Whereas APC methylation in EC was similar to that in BE (P = 0.052), it was not
associated with tumor stage (P = 0.204).
Additionally, APC methylation was not significantly associated with overall
survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) in patients with EC. The
performance of APC methylation for the detection of EC and BE achieved areas
under the receiver operating characteristic curves of 0.94 and 0.88,
respectively.
Conclusion: Our results imply that APC methylation detection
is a potential diagnostic biomarker for EC and BE.
Keywords: esophageal
cancer, Barrett’s esophagus, methylation, APC