108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基质金属蛋白酶 3 基因多态性 rs679620 和 rs3025058 与缺血性卒中患病风险的关系:一项荟萃分析
Authors Zhang Q
Received 21 September 2017
Accepted for publication 11 December 2017
Published 31 January 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 419—427
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S152256
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Purpose: The
relationship of the matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3 )
polymorphisms rs679620 and rs3025058 with ischemic stroke has received much
attention. The aim of the present study was to perform a meta-analysis of
published case–control studies to evaluate the cumulative evidence.
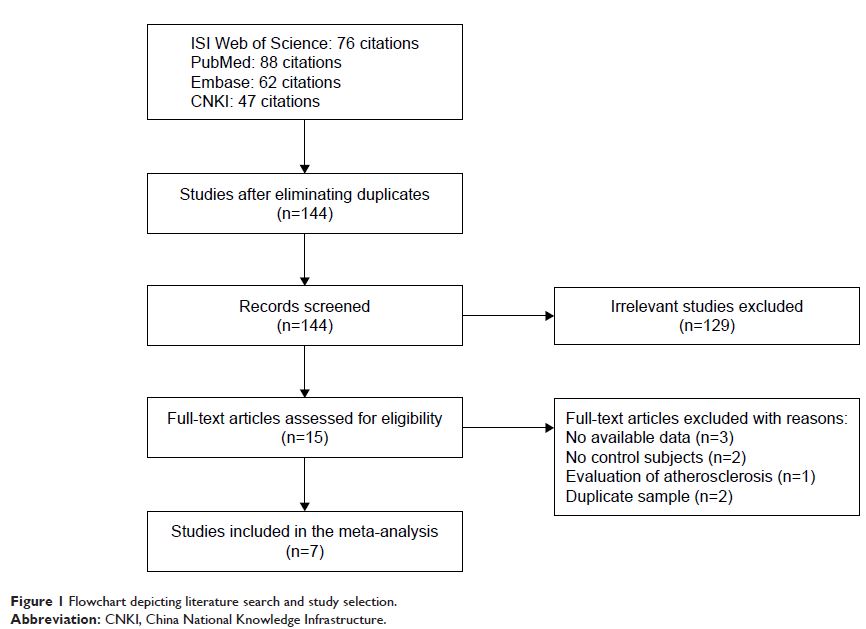
Methods: We performed a search of ISI Web of Science, Embase, PubMed, and
China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases. Pooled odds ratios (ORs)
were appropriately derived from fixed-effects or random-effects models.
Results: We identified seven eligible studies including 5,204 subjects. The
pooled analysis showed that the MMP-3 rs679620
A allele carriers had increased risk of ischemic stroke compared with
homozygotes for the G allele in Asians (AA + GA vs GG: OR =1.42, 95% CI:
1.05–1.91, P =0.022). Concerning the rs3025058
polymorphism, the results did not suggest an association between rs3025058
genotypes and ischemic stroke risk (5A5A + 6A5A vs 6A6A: OR =1.04, 95% CI:
0.73–1.47, P =0.844; 5A5A vs 6A5A + 6A6A: OR
=1.14, 95% CI: 0.74–1.77, P =0.556; and 5A5A
vs 6A6A: OR =1.11, 95% CI: 0.68–1.80, P =0.677). In
subgroup analysis by ethnicity, no statistically significant associations were
demonstrated for rs3025058 in Asians and Caucasians, respectively. There was no
evidence for publication bias.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that the rs679620 A allele carriers have increased
risk of ischemic stroke in Asians, but there is no association between
rs3025058 and ischemic stroke risk.
Keywords: ischemic stroke, meta-analysis, MMP-3, polymorphism