108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

YKL-40 蛋白是 COPD 潜在的生物标志物:荟萃分析和系统评价
Authors Tong X, Wang D, Liu S, Ma Y, Li Z, Tian P, Fan H
Received 27 September 2017
Accepted for publication 19 December 2017
Published 30 January 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 409—418
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S152655
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Background: Many
studies have found that YKL-40 may play an important pathogenic role in COPD.
However, the results of these studies were inconsistent. Therefore, we
performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the role of
YKL-40 in COPD.
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search in many database and
commercial internet search engines to identify studies involving the role of
YKL-40 in patients with COPD. The standardized mean difference (SMD) and
Fisher’s Z-value with its 95% confidence
interval (CI) were used to investigate the effect sizes.
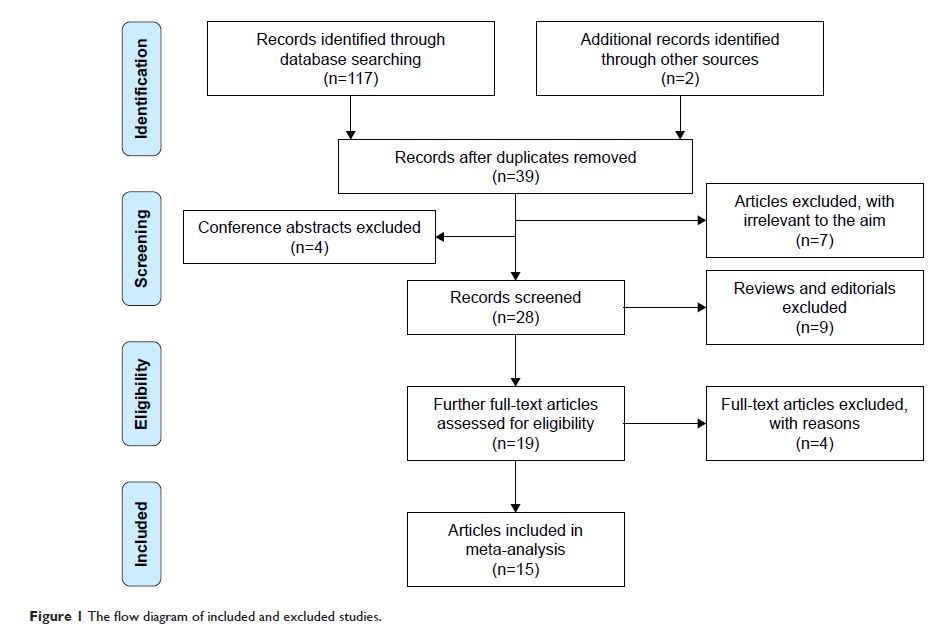
Results: A total of 15 eligible articles including 16 case–control/cohort
groups were included in the meta-analysis. The results indicated that the serum
YKL-40 levels in patients with COPD were significantly higher than those in
healthy controls (SMD =1.58, 95% CI =0.68–2.49, P =0.001), and it was correlated
with lung function (pooled r =-0.32; Z =-0.33; P <0.001). The results of
subgroup analysis found that the serum YKL-40 levels were statistically
different between the exacerbation group and the stable group in patients with
COPD (SMD =1.55, 95% CI =0.81–2.30, P <0.001).
Moreover, the results indicated that the sputum YKL-40 levels in patients with
COPD were also significantly higher than those in healthy controls (SMD =0.70,
95% CI =0.10–1.30, P =0.022).
Conclusion: The current study suggests that YKL-40 may be implicated in
bronchial inflammation and remodeling in COPD and may be considered as a useful
biomarker for COPD diagnosis and monitoring.
Keywords: YKL-40, COPD, biomarker, meta-analysis