108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

共聚物胶束作为 pH 敏感性纳米载体,增强 HER2 阳性乳腺癌细胞中 HER2 适配体的细胞毒性
Authors Shen Y, Zhang J, Hao W, Wang T, Liu J, Xie Y, Xu S, Liu H
Received 25 August 2017
Accepted for publication 22 October 2017
Published 25 January 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 537—553
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S149942
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Efficient delivery of nucleic acids into target cells is crucial for
nucleic acid-based therapies. Various nucleic acid delivery systems have been
developed, each with its own advantages and limitations. We previously
developed a nanoparticle-based delivery system for small chemical drugs using
pH-responsive PEG8-PDPA100-PEG8 polymer
micelles as carriers. In this study, we extend the application of these
pH-responsive micelle-like nanoparticles (MNPs) to deliver oligonucleotides. We
demonstrate that the MNPs efficiently encapsulate and deliver oligonucleotides
of different lengths (20–100 nt) into cells. The cargo oligonucleotides
are rapidly released at pH 5.0. We prepared MNPs carrying a Texas
red-fluorescently labeled anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)
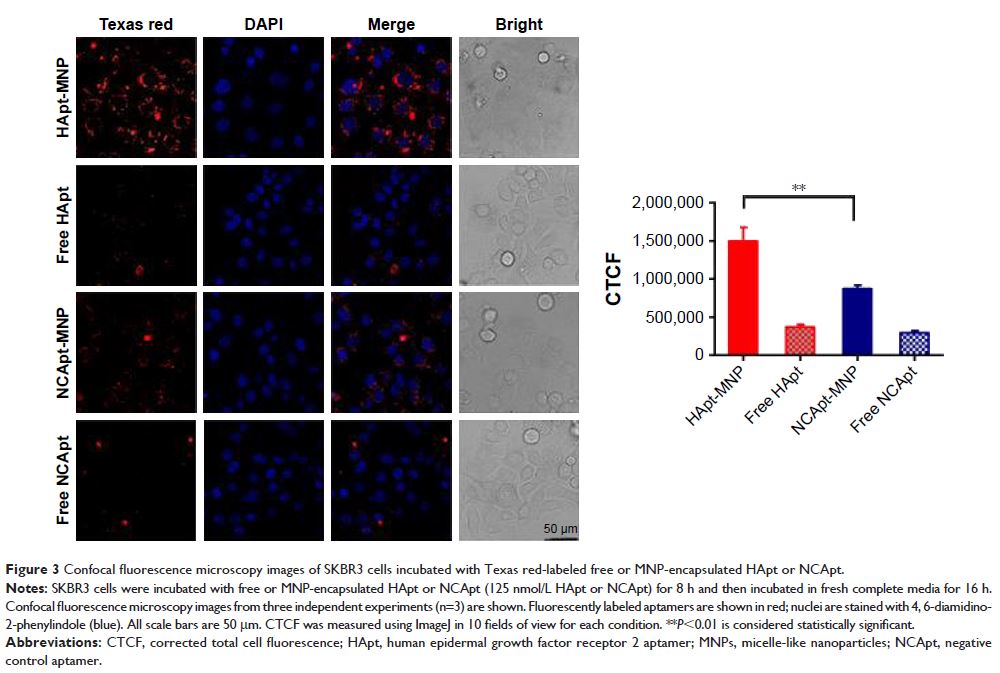
aptamer (HApt). Compared to free HApt, the HApt-MNPs resulted in significantly
better cellular uptake, reduced cell viability, and increased apoptosis in
SKBR3 breast cancer cells, which overexpress HER2. Moreover, HApt-MNPs were
significantly less cytotoxic to MCF7 breast cancer cells, which express low
levels of HER2. After cellular uptake, HApt-MNPs mainly accumulated in
lysosomes; inhibition of lysosomal activity using bafilomycin A1 and
LysoTracker Red staining confirmed that lysosomal activity and low pH were
required for HApt-MNP accumulation and release. Furthermore, HER2 protein
expression declined significantly following treatment with HApt-MNPs in SKBR3
cells, indicating that HApt-induced translocation of HER2 to lysosomes exerted
a potent cytotoxic effect by altering signaling downstream of HER2. In
conclusion, this pH-responsive and lysosome-targeting nanoparticle system can
efficiently deliver oligonucleotides to specific target cells and has
significant potential for nucleic acid-based cancer therapies.
Keywords: pH-responsive
micelle-like nanoparticles, nucleic acid delivery, HER2-targeted therapy