108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

与多发性肌炎和皮肌炎相关的静脉血栓栓塞患病风险的增加:一项荟萃分析
Authors Li Y, Wang P, Li L, Wang F, Liu Y
Received 15 November 2017
Accepted for publication 8 December 2017
Published 23 January 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 157—165
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S157085
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
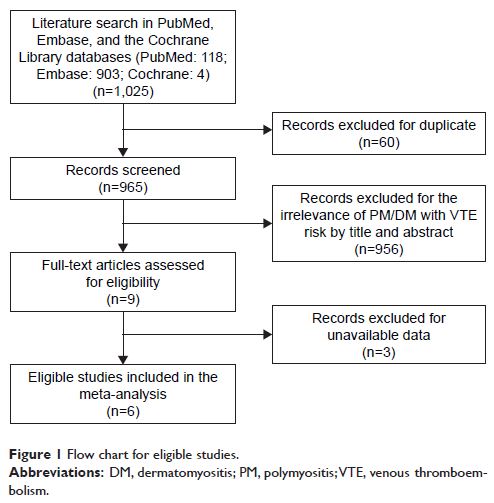
Objective: Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (PM/DM) have been implicated in the
development of venous thromboembolism (VTE). Previous studies investigating the
association between PM/DM and VTE risk had yielded inconsistent findings. The
aim of this study was to precisely estimate this association by meta-analysis
of all available publications.
Methods: Two investigators independently performed a comprehensive
literature search in databases of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library
for eligible studies. The strength for the association was weighed by pooled
odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Stratified analysis
and sensitivity analysis were performed for further analysis.
Results: Six studies including 9,045 patients with PM/DM were analyzed. The
pooled OR suggested that inflammatory myositis was associated with increased
risk of VTE (OR =4.31, 95% CI: 2.55–7.29, P <0.001).
Besides, significantly elevated risk of VTE was related with PM and DM,
respectively (for PM: OR =6.87, 95% CI: 4.12–11.46, P <0.001; for DM: OR =11.59, 95%
CI: 6.54–20.55, P <0.001). In
addition, inflammatory myositis could increase the risk of DVT (OR =4.85, 95%
CI: 1.38–17.12, P <0.05) and PE
(OR =4.74, 95% CI: 2.18–10.30, P <0.05).
Sensitivity analysis did not materially alter the pooled results.
Conclusion: Our study shows strong evidence that patients with inflammatory myositis
have an increased risk of VTE.
Keywords: polymyositis, dermatomyositis, venous thromboembolism, deep venous
thrombosis, pulmonary embolism