108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

弓形虫来源 exosomes 的生物学特性及其免疫调节功能的研究
Authors Li Y, Liu Y, Xiu F, Wang J, Cong H, He S, Shi Y, Wang X, Li X, Zhou H
Received 7 September 2017
Accepted for publication 8 December 2017
Published 19 January 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 467—477
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S151110
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
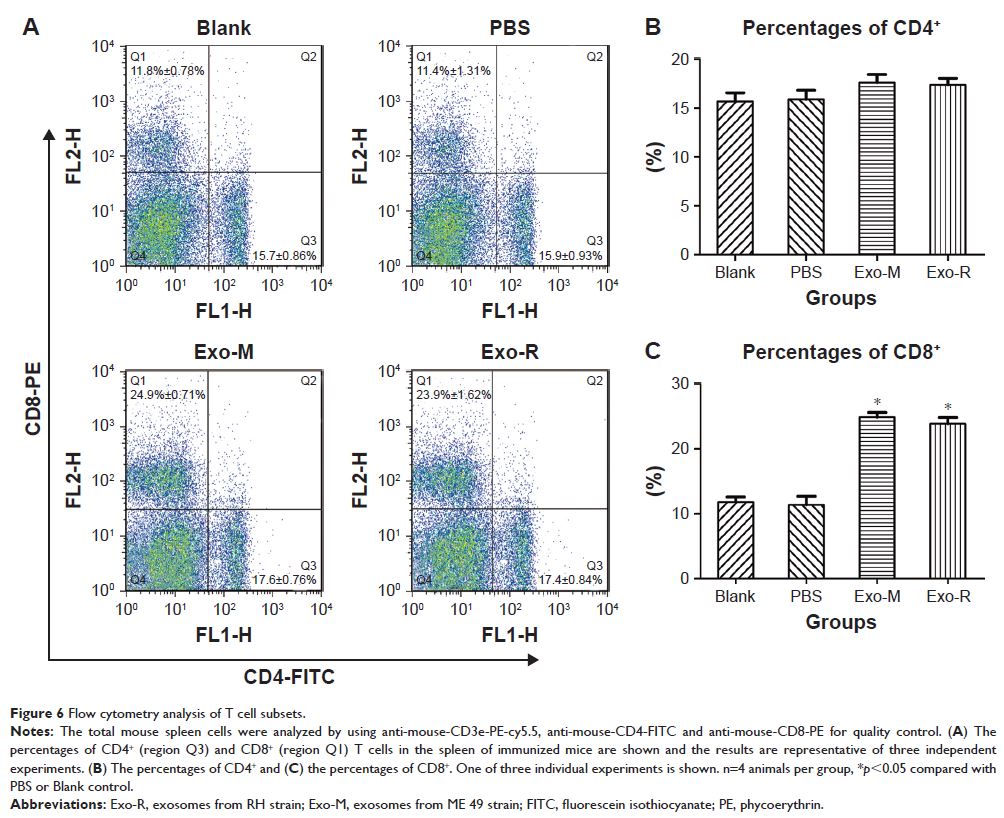
摘要:Exosomes 是由细胞内的多囊泡体与细胞膜融合释放到细胞外的双层膜性纳米小囊泡。绝大多数类型的活细胞均可产生 exosomes,参与细胞间通讯、细胞迁移、免疫调节等诸多过程。目前,对弓形虫来源的 exosomes 及其生物学特性与功能的研究还非常有限。为此,我们从弓形虫速殖子培养上清液中分离提取微小囊泡,经 TEM、NanoSight 和 Western blotting 分析其形态、大小和结构以及表面标记,可鉴定为弓形虫来源的 exosomes。在体外,弓形虫 exosomes 与巨噬细胞 RAW264.7 融合并调节其分泌细胞因子水平,表现为 IL-12、TNF-α 和 IFN-γ 升高。在体内,弓形虫 exosomes 诱导 BALB/c 小鼠产生较高水平的 IFN-γ、IL-12、IgG、IgG2a 和 CD8+T,发挥特异性的细胞免疫和体液免疫作用,并能延长感染小鼠的存活时间,有一定的抗弓形虫免疫保护力。综上研究表明,弓形虫可产生并分泌 exosomes,具有免疫应答与调节功能,提示弓形虫 exosomes 可能是抗弓形虫病疫苗或药物候选靶标。
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii , exosomes,
macrophage, mouse, immune response