108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA H19 在卵巢癌细胞中起到 miR-370-3p 竞争性内源性 RNA 的作用,促进转化生长因子-β 诱导的上皮 - 间质转化
Authors Li J, Huang YY, Deng XJ, Luo ML, Wang XF, Hu HY, Liu CD, Zhong M
Received 24 August 2017
Accepted for publication 31 October 2017
Published 18 January 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 427—440
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149908
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
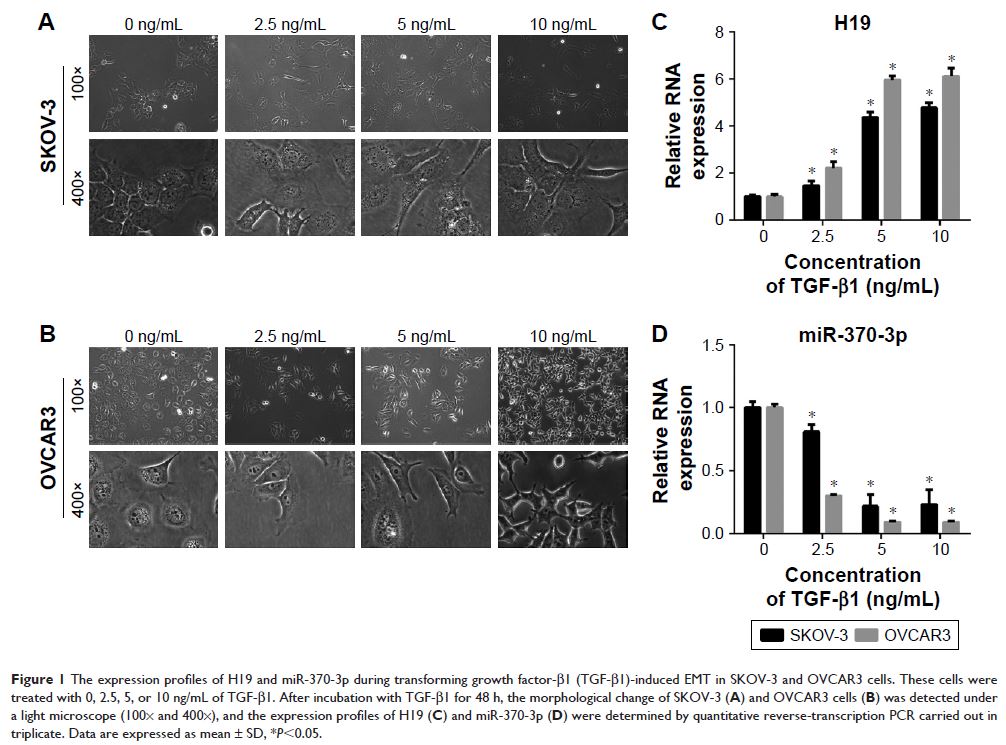
Abstract: Ovarian cancer is a
gynecological malignant tumor with a high mortality rate among women, owing to
metastatic progression and recurrence. Acquisition of invasiveness is
accompanied by the loss of epithelial features and a gain of a mesenchymal
phenotype, a process known as epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). Transforming
growth factor-β (TGF-β) has been implicated in the regulation of EMT. In the
present study, we aimed to investigate the role of long noncoding RNA H19 and
microRNA-370 (miR-370-3p) in TGF-β-induced EMT. Ovarian cancer cell lines
SKOV-3 and OVCAR3 were incubated with different concentrations of TGF-β, and
the results showed that TGF-β treatment upregulated H19 and downregulated
miR-370-3p. In addition, an H19 knockdown or miR-370-3p overexpression
suppressed TGF-β-induced EMT, while H19 overexpression or a miR-370-3p
knockdown promoted TGF-β-induced EMT. Mechanistically, H19 could directly bind
to miR-370-3p and effectively act as its competing endogenous RNA. Furthermore,
we demonstrated that this activity of H19 was involved in its promotion of TGF-β-induced
EMT. Thus, our results may provide novel insights into the process of
TGF-β-induced EMT.
Keywords: transforming
growth factor-β, long noncoding RNA H19, microRNA-370-3p, competing endogenous
RNA, epithelial–mesenchymal transition