108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
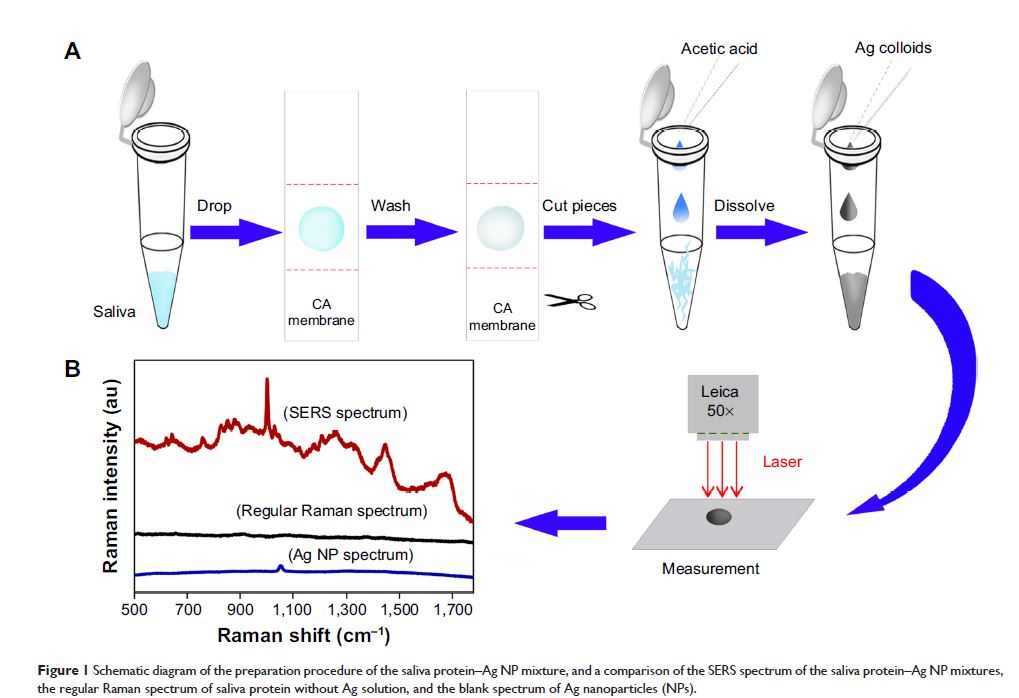
唾液蛋白对乳腺良、恶性肿瘤的无创性分化的表面增强拉曼光谱
Authors Feng S, Huang S, Lin D, Chen G, Xu Y, Li Y, Huang Z, Pan J, Chen R, Zeng H
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 537—547
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S71811
Received 26 July 2014, Accepted 25 October 2014, Published 12 January 2015
Abstract: The capability of saliva protein analysis, based on membrane protein
purification and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), for detecting
benign and malignant breast tumors is presented in this paper. A total of 97
SERS spectra from purified saliva proteins were acquired from samples obtained
from three groups: 33 healthy subjects; 33 patients with benign breast tumors;
and 31 patients with malignant breast tumors. Subtle but discernible changes in
the mean SERS spectra of the three groups were observed. Tentative assignments
of the saliva protein SERS spectra demonstrated that benign and malignant
breast tumors led to several specific biomolecular changes of the saliva
proteins. Multiclass partial least squares–discriminant analysis was utilized
to analyze and classify the saliva protein SERS spectra from healthy subjects,
benign breast tumor patients, and malignant breast tumor patients, yielding
diagnostic sensitivities of 75.75%, 72.73%, and 74.19%, as well as
specificities of 93.75%, 81.25%, and 86.36%, respectively. The results from
this exploratory work demonstrate that saliva protein SERS analysis combined
with partial least squares–discriminant analysis diagnostic algorithms has
great potential for the noninvasive and label-free detection of breast cancer.
Keywords: SERS, saliva protein purification, PLS-DA, breast cancer, noninvasive detection
Keywords: SERS, saliva protein purification, PLS-DA, breast cancer, noninvasive detection