108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

表小檗碱的口服生物利用度、排泄和细胞色素 P450 抑制性能:一个体内和体外评价
Authors Chen N, Yang X, Guo C, Bi X, Chen J, Chen H, Li H, Lin H, Zhang Y
Received 14 September 2017
Accepted for publication 14 November 2017
Published 28 December 2017 Volume 2018:12 Pages 57—65
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S151660
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rammohan Devulapally
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Frank Boeckler
Abstract: Epiberberine (EPI) is a novel
and potentially effective therapeutic and preventive agent for diabetes and
cardiovascular disease. To evaluate its potential value for drug development, a
specific, sensitive and robust high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem
mass spectrometry assay for the determination of EPI in rat biological samples
was established. This assay was used to study the pharmacokinetics,
bioavailability and excretion of EPI in rats after oral administration. In
addition, a cocktail method was used to compare the inhibition characteristics
of EPI on cytochrome P450 (CYP450) isoforms in human liver microsomes (HLMs)
and rat liver microsomes (RLMs). The results demonstrated that EPI was rapidly
absorbed and metabolized after oral administration (10, 54 or 81 mg/kg) in
rats, with T max of
0.37–0.42 h and T 1/2 of 0.49–2.73 h. The C max and area
under the curve values for EPI increased proportionally with the dose, and the
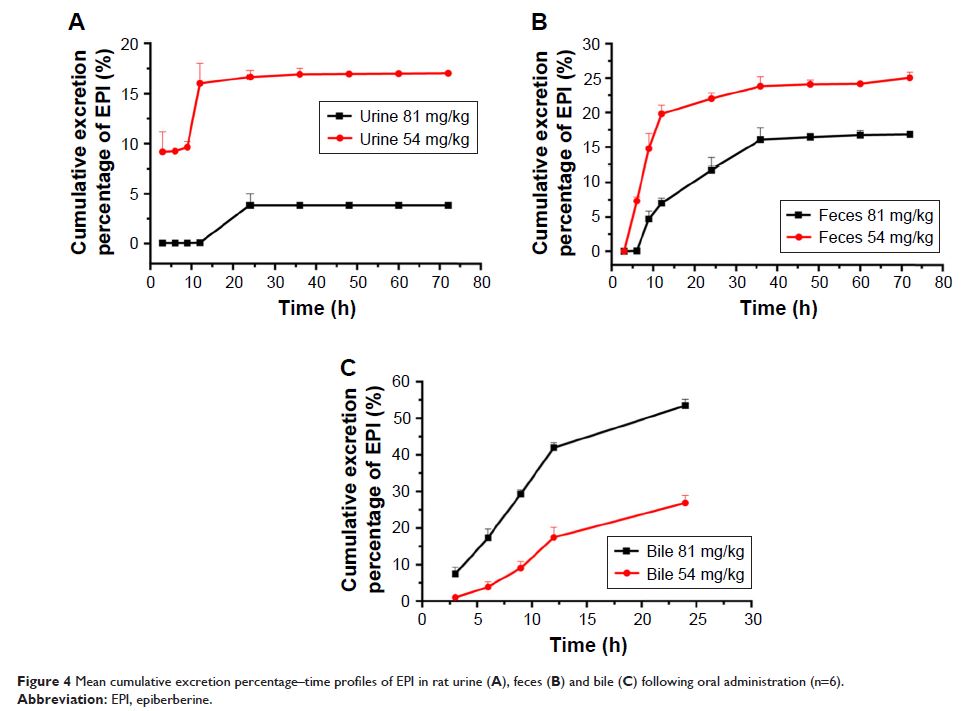
oral absolute bioavailability was 14.46%. EPI was excreted mainly in bile and
feces, and after its oral administration to rats, EPI was eliminated
predominantly by the kidneys. A comparison of the current half-maximal
inhibitory concentration and Ki values revealed that EPI demonstrated an obvious
inhibitory effect on CYP2C9 and CYP2D6. Furthermore, its effect was stronger in
HLM than in RLM, more likely to be a result of noncompetitive inhibition.
Keywords: epiberberine,
bioavailability, excretion kinetics, CYP inhibition type