108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

老年重型缺血性卒中后抑郁症患者的血清尿酸和总胆红素的变化
Authors Gao J, Xu W, Han K, Zhu L, Gao L, Shang XL
Received 25 August 2017
Accepted for publication 9 November 2017
Published 27 December 2017 Volume 2018:14 Pages 83—93
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S149712
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Background: This was a longitudinal study which investigated the relationship
between serum uric acid (SUA) and total bilirubin (Tbil) upon admission in
elderly stroke patients and the occurrence of postischemic stroke depression
(IPSD) at 3, 6, and 9 months of post-stroke follow-up.
Subjects and methods: Data were analyzed for 525 acute ischemic stroke
patients. Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores >17 and Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders , Fourth Edition (DSM-IV ) were used separately to
screen and diagnose IPSD at 3, 6, and 9 months post-stroke. Once IPSD was
diagnosed, follow-up activities were terminated.
Results: High levels of SUA (odds ratio [OR]=2.08, P <0.01) and Tbil
(OR=2.31, P <0.01) in the first 3 months
post-stroke and low levels of SUA (OR=2.05, P =0.03)
and Tbil (OR=2.79, P <0.01) from 3
to 6 months post-stroke were identified as risk factors for major IPSD. At 3
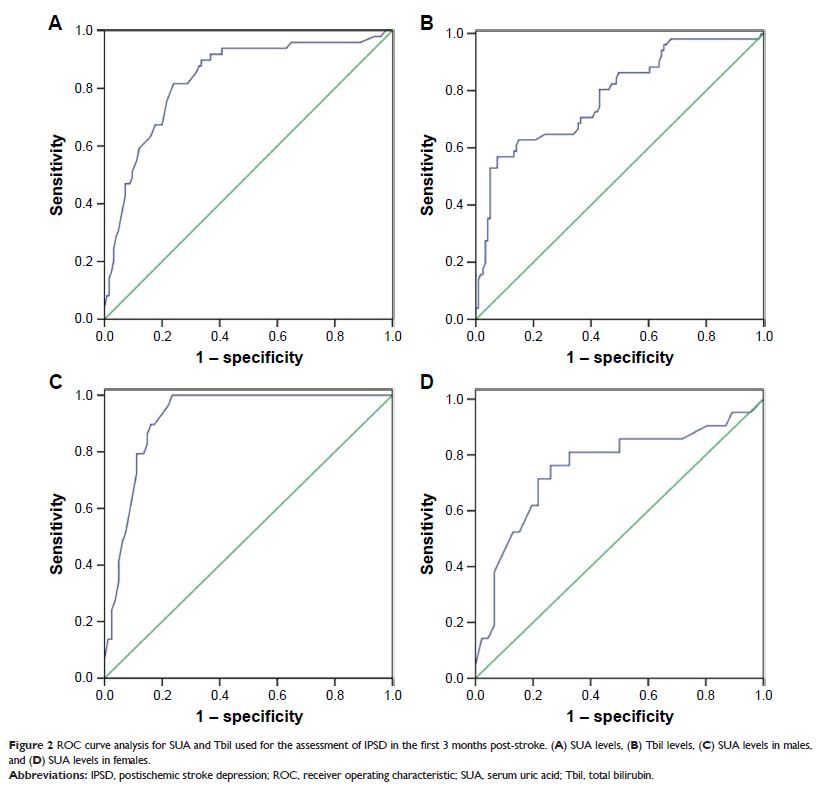
months, patients with SUA levels ≥406.5 µmol/L (males with SUA levels of ≥409.5
µmol/L and females with SUA levels ≥385.5 µmol/L) and Tbil levels ≥23.65 µmol/L
were more likely to develop major IPSD. At 6 months, both SUA (area under curve
[AUC]=0.625, P =0.005, cutoff =194.0 µmol/L) and
Tbil (AUC=0.681, P =0.004, cutoff
=6.75 µmol/L) had minor diagnostic values (AUC<0.700), although SUA levels
≤214.5 µmol/L (AUC=0.756, P =0.001) in female
patients had a good diagnostic value (AUC=0.722, P =0.006) for major IPSD. At 9
months, major IPSD showed no statistical relationship with either SUA (χ 2=2.33, P =0.13) or Tbil (χ 2=0.41, P =0.84).
Conclusion: Higher levels of SUA and Tbil on admission were
closely related to the occurrence of major IPSD within 3 months of stroke.
Lower levels of these two biomarkers on admission were characteristic for the
occurrence of major IPSD between 3 and 6 months post-stroke, while 6 months
after stroke, there was no relationship between major IPSD and these two
biomarkers.
Keywords: depression
after stroke, stroke, total bilirubin, uric acid, longitudinal study