108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

药物干预对中国医院的质子泵抑制剂合理使用的影响
Authors Xin C, Dong Z, Lin M, Li G
Received 30 August 2017
Accepted for publication 10 November 2017
Published 27 December 2017 Volume 2018:12 Pages 21—26
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S150388
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Background: The prescriptions of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have raised
concern due to both huge increase in medical expenditure and the possible
long-term adverse events caused by them; therefore, an approach to taper off
the irrational use of PPIs by patients is clinically warranted. The aim of this
study was to evaluate the impact of pharmaceutical interventions on the
rational use of PPIs.
Patients and methods: A single-center, pre- to post-intervention study
(pharmaceutical interventions group and control group) was performed in a
Chinese hospital. Pharmaceutical interventions were performed in the
post-intervention group, including educative group activities, real-time
monitoring of clinical records and making recommendations to doctors on PPI
prescriptions based on the criteria set at the beginning of the study. The
number of patients with rational indication, the accuracy rate of
administration route, the duration of therapy and the changes in total PPI
costs, mean PPI costs, mean total drug costs and mean hospitalization costs
were the main outcome measures.
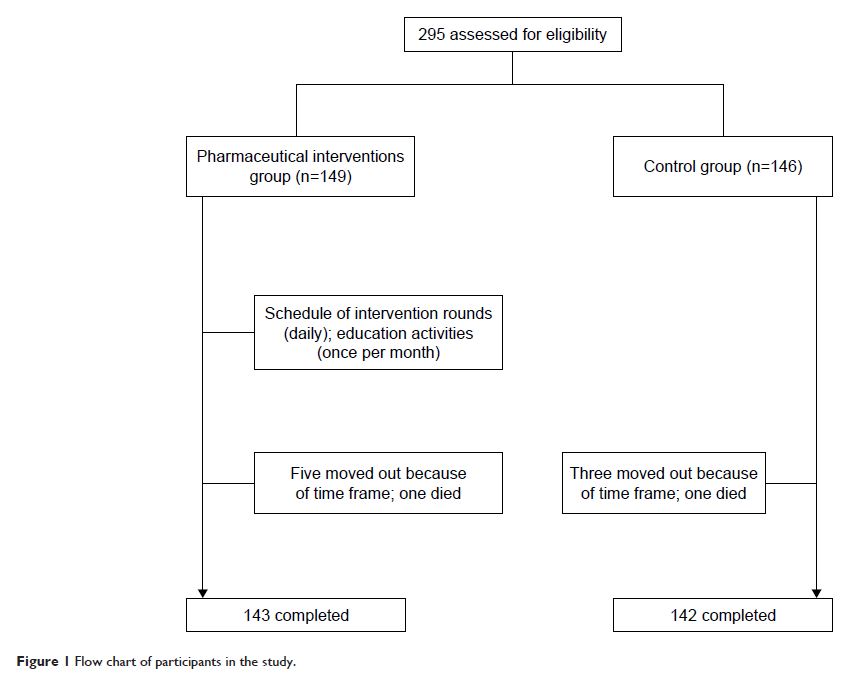
Results: A total of 285 patients were included in the study.
After 6 months of interventions, significant improvements in the number of
patients with rational indication were found (96.5% in the pharmaceutical
interventions group vs 71.8% in the control group, P <0.01). The accuracy rate of
administration route was increased (99.3% vs 73.2%, P <0.05), while the duration of
therapy was decreased (7.9±0.5 vs 14.3±0.8, P <0.01).
Pharmaceutical interventions led to significant reductions in mean PPIs costs,
mean total drug costs and mean hospitalization costs (P <0.001).
Conclusion: This study provides important evidence on the
beneficial effect of pharmaceutical interventions on enhancing the rational use
of PPIs and substantial cost saving by increasing the number of patients with
rational indication and reducing the risk for long-term adverse events.
Keywords: proton pump
inhibitors, pharmaceutical interventions, clinical pharmacist, indications,
cost saving