108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过遏制 MMP-2/MMP-9 表达,利用 CuS@mSiO2-PEG 纳米粒子抑制癌细胞迁移
Authors Deng G, Zhou F, Wu Z, Zhang F, Niu K, Kang Y, Liu X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Wang Q
Received 7 August 2017
Accepted for publication 17 September 2017
Published 21 December 2017 Volume 2018:13 Pages 103—116
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S148487
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: The metastasis of cancer cells is a vital aspect of disease
progression and therapy. Although a few nanoparticles (NPs) aimed at
controlling metastasis in cancer therapy have been reported, the NPs are
normally combined with drugs, yet the direct therapeutic effects of the NPs are
not reported. To study the direct influence of NPs on cancer metastasis, the
potential suppression capacity of CuS@mSiO2-PEG NPs to tumor
cell migration, a kind of typical photothermal NPs, was systemically evaluated
in this study. Using CuS@mSiO2-PEG NP stimulation
and a transwell migration assay, we found that the migration of HeLa cells was
significantly decreased. This phenomenon may be associated with two classical
proteins in metastasis: matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). In addition, the mechanism may closely associate
with non-receptor tyrosine kinase protein (SRC)/focal adhesion kinase (FAK)
signaling pathway which varies in vivo and in vitro. To confirm the differences
in the expression of SRC and FAK, related inhibitors were studied for
additional comparison. Also, the results indicated that even though the
migration inhibition was closely related to SRC and FAK signaling pathway,
there may be another unknown regulation mechanism existing and its metastasis
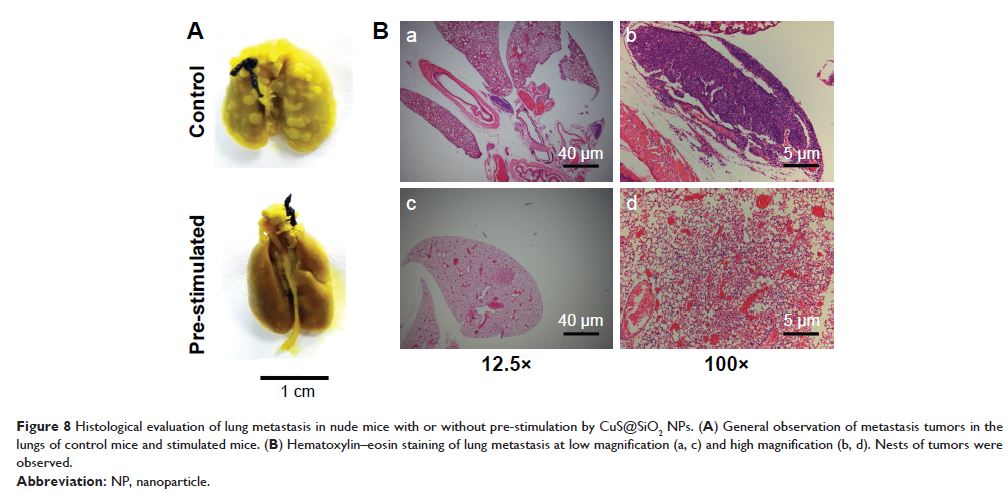
inhibition was significant. Confirmed by long-term survival curve study,
CuS@mSiO2-PEG NPs significantly reduced the metastasis of
cancer cells and improved the survival rates of metastasis in a mouse model.
Thus, we believe that the direct influence of NPs on cancer cell metastasis is
a promising study topic.
Keywords: metastasis
inhibition, photothermal nanoparticles, SRC/FAK signaling pathway, survival
curves, MMPs