108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

重度抑郁症患者的血浆补体成分 4 增加
Authors Wei J, Liu Y, Zhao L, Yang X, Ni P, Wang Y, Li T, Ma X
Received 8 September 2017
Accepted for publication 13 November 2017
Published 20 December 2017 Volume 2018:14 Pages 37—41
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S151238
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Abstract: Elevation of plasma
inflammatory factors in major depressive disorder (MDD) has been repeatedly
observed, but contradictory results have also been reported. Alteration of
complement components in MDD may also contribute to the pathophysiology of MDD
by participating in inflammation. The recent findings that complement component
4 (C4) was involved in neural synapse elimination and associated with
schizophrenia implicated the potential roles of C4 in MDD. In this study, we
analyzed the plasma concentration of complement C4 and inflammatory factors,
including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, interferon-α, interferon-γ
and tumor necrosis factor-α, of 53 patients with MDD and 60 healthy individuals.
The plasma of 17 patients out of 51 after antidepressant medication was also
collected for analysis. The results showed that peripheral C4 in MDD was higher
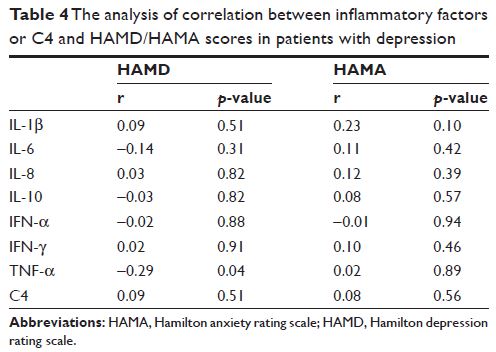
than that in healthy controls. No significant correlation of inflammatory
factors or C4 with depressive or anxiety symptoms was found. Antidepressant
medication significantly reduced plasma C4 of patients with MDD. Our results
were consistent with previous findings that complement components were elevated
in MDD and suggested that C4 might play a role in pathophysiology of MDD and
could be a candidate in the research of biomarker and the pathophysiology of
MDD.
Keywords: depression, C4,
inflammation