108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过基于原子力显微镜的纳米检测法检测达卡巴嗪对活黑色素瘤细胞中 CD44 的影响
Authors Huang X, He JX, Zhang HT, Sun K, Yang J, Wang HJ, Zhang HX, Guo ZZ, Zha ZG, Zhou CR
Received 14 August 2017
Accepted for publication 10 November 2017
Published 18 December 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 8867—8886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S149107
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
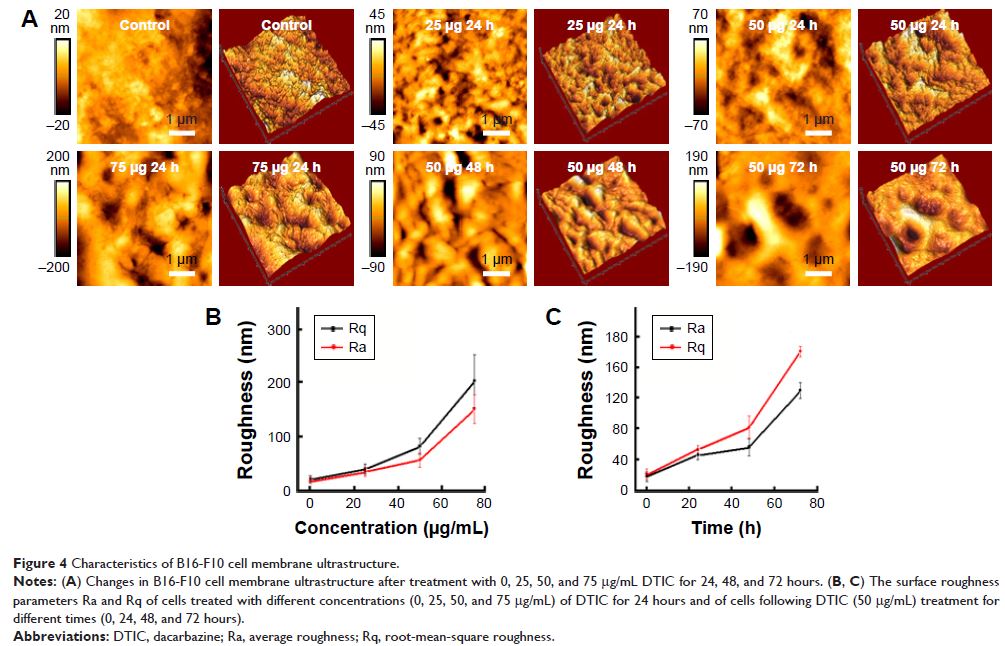
Abstract: CD44 ligand–receptor interactions are known to be involved in
regulating cell migration and tumor cell metastasis. High expression levels of
CD44 correlate with a poor prognosis of melanoma patients. In order to
understand not only the mechanistic basis for dacarbazine (DTIC)-based melanoma
treatment but also the reason for the poor prognosis of melanoma patients
treated with DTIC, dynamic force spectroscopy was used to structurally map
single native CD44-coupled receptors on the surface of melanoma cells. The
effect of DTIC treatment was quantified by the dynamic binding strength and the
ligand-binding free-energy landscape. The results demonstrated no obvious
effect of DTIC on the unbinding force between CD44 ligand and its receptor,
even when the CD44 nanodomains were reduced significantly. However, DTIC did
perturb the kinetic and thermodynamic interactions of the CD44 ligand–receptor,
with a resultant greater dissociation rate, lower affinity, lower binding free
energy, and a narrower energy valley for the free-energy landscape. For cells
treated with 25 and 75 µg/mL DTIC for 24 hours, the dissociation constant
for CD44 increased 9- and 70-fold, respectively. The CD44 ligand binding free
energy decreased from 9.94 for untreated cells to 8.65 and 7.39 kcal/mol
for DTIC-treated cells, which indicated that the CD44 ligand–receptor complexes
on DTIC-treated melanoma cells were less stable than on untreated cells.
However, affinity remained in the micromolar range, rather than the millimolar
range associated with nonaffinity ligands. Hence, the CD44 receptor could still
be activated, resulting in intracellular signaling that could trigger a
cellular response. These results demonstrate DTIC perturbs, but not completely
inhibits, the binding of CD44 ligand to membrane receptors, suggesting a basis
for the poor prognosis associated with DTIC treatment of melanoma. Overall,
atomic force microscopy-based nanoscopic methods offer thermodynamic and
kinetic insight into the effect of DTIC on the CD44 ligand-binding process.
Keywords: atomic force microscopy, tumor, dynamic force spectroscopy,
kinetic and thermodynamic interactions, affinity, nanoindentation