108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:开发厄洛替尼纳米脂质体制剂用于肺癌治疗和体外/体内抗肿瘤评估
Authors Zhou X, Tao H, Shi KH
Received 21 July 2017
Accepted for publication 18 October 2017
Published 18 December 2017 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1—8
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S146925
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
***本文章已被撤回***
Abstract: The aim of this study
was to develop PEGylation liposomes formulations of erlotinib and evaluate
their characteristics, stability, and release characteristics. The average
particle sizes and entrapment efficiency of PEGylation erlotinib liposomes are
102.4±3.1 nm and 85.3%±1.8%, respectively. Transmission electron
microscopy images showed that the liposomes dispersed well with a uniform shape
and no changes during the storage. The in vitro drug-release kinetic model
of erlotinib release from the PEGylation liposomes in phosphate-buffered saline
fit well with the Higuchi equation. In vitro anticancer activity assay showed
that the blank liposomes had lower cellular cytotoxicity and that the cellular
cytotoxicity of erlotinib liposomes increased significantly under the same
incubation condition, which should contribute to the increase in intracellular
drug concentration by the transportation of liposomes. The two liposomes of
erlotinib (with and without PEGylation) exhibited similar cellular cytotoxicity
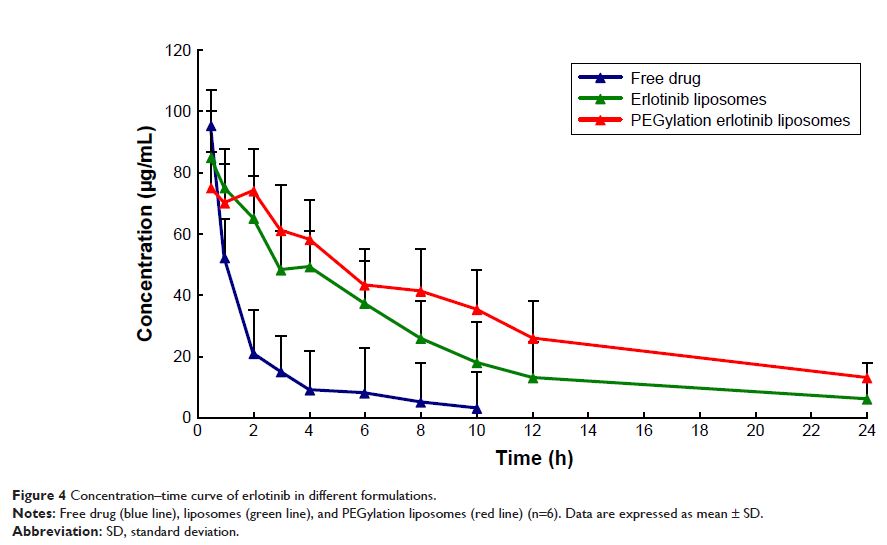
with no significantly different concentrations. Pharmacokinetic results
indicated that erlotinib-loaded PEGylation liposomes can significantly change
the pharmacokinetic behavior of drugs and improve the drug bioavailability by
nearly 2 times compared to ordinary liposomes. No sign of damages such as the
appearance of epithelial necrosis or sloughing of epithelial cells was detected
in histological studies.
Keywords: cellular
cytotoxicity, drug-release, erlotinib, PEGylation liposomes, pharmacokinetic