108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

程序性死亡配体 1 表达与 CD8 + T 细胞浸润减少和预测肛门鳞状细胞癌患者预后不良有关
Authors Zhao Y, Sun WP, Peng J, Deng Y, Fang Y, Huang J, Zhang H, Wan D, Lin J, Pan Z
Received 13 October 2017
Accepted for publication 22 November 2017
Published 18 December 2017 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1—11
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S153965
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Alexandra Fernandes
Objective: Increased expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) on tumor
cells can be found in various malignancies; however, very limited information
is known about its role in anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC). This study
explored PD-L1 expression in ASCC patients and its association with patients’
clinicopathological features, CD8+ T cell infiltration, and prognosis.
Methods: Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor samples
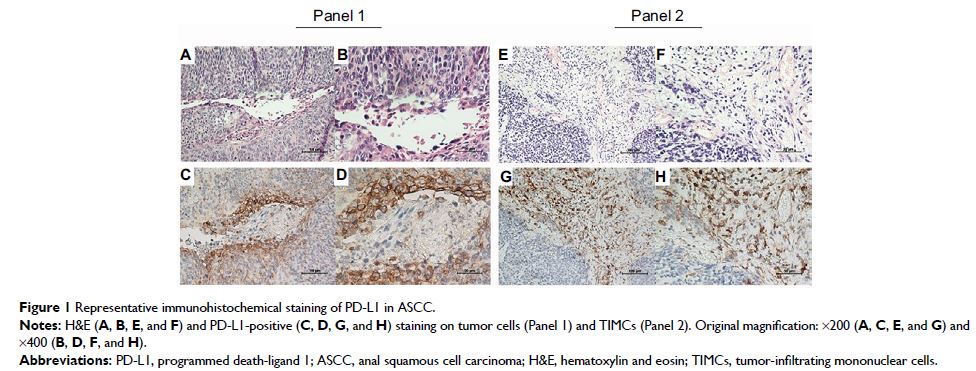
from 26 patients with ASCC were retrieved. The levels of PD-L1 expression on
the membrane of both tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating mononuclear cells
(TIMCs) were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. CD8+ T cell densities, both
within tumors and at the tumor–stromal interface, were also analyzed. Baseline
clinicopathological characteristics, human papilloma virus (HPV) status, and
outcome data correlated with PD-L1-positive staining.
Results: PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and TIMCs was observed
in 46% and 50% of patients, respectively. Nineteen patients (73%) were HPV
positive, with 7 showing PD-L1-positive staining on tumor cells and 9 showing
PD-L1-positive staining on TIMCs. Increasing CD8+ density within tumors, but
not immune stroma, was significantly associated with decreased PD-L1 expression
by both tumor cells and TIMCs (P =0.0043 and P =0.0007). Patients with negative
PD-L1 expression had significantly better progression-free survival (P =0.038 and P =0.0443) and a non-statistically
significant trend toward longer overall survival (P =0.0882
and P =0.1222) compared with patients
with positive PD-L1 expression.
Conclusion: PD-L1 is widely expressed on the membrane of
tumor cells and TIMCs in ASCCs. Its negative impact on prognosis may be due to
the diminished CD8+ T cell infiltration within tumors.
Keywords: CD8, PD-L1,
HPV, tumor infiltrating mononuclear cells