108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胆酸钠增强的聚合物胶束系统用于肿瘤靶向递送紫杉醇
Authors Zhang X, Wu Y, Zhang M, Mao J, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Yao J, Xu C, Guo W, Yu B
Received 28 August 2017
Accepted for publication 10 November 2017
Published 13 December 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 8779—8799
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S150196
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
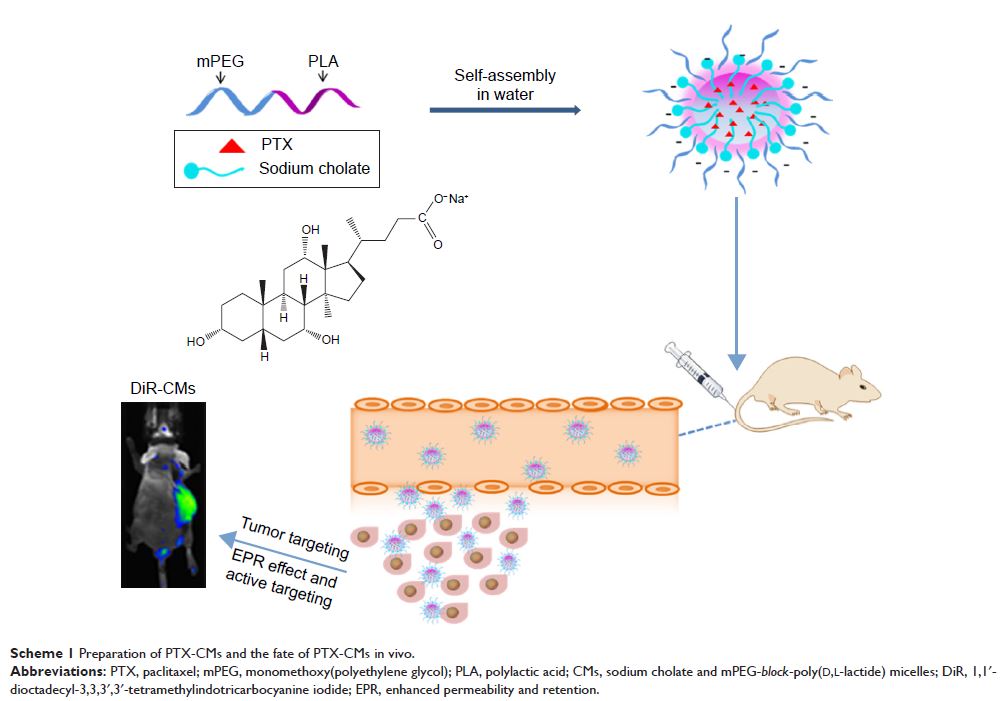
Purpose: Polymeric micelles are attractive nanocarriers for tumor-targeted
delivery of paclitaxel (PTX). High antitumor efficacy and low toxicity require
that PTX mainly accumulated in tumors with little drug exposure to normal
tissues. However, many PTX-loaded micelle formulations suffer from low
stability, fast drug release, and lack of tumor-targeting capability in the
circulation. To overcome these challenges, we developed a micellar formulation
that consists of sodium cholate (NaC) and monomethoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-block -poly (D,L-lactide)
(mPEG-PDLLA).
Methods: PTX-loaded NaC-mPEG-PDLLA micelles (PTX-CMs) and PTX-loaded
mPEG-PDLLA micelles (PTX-Ms) were formulated, and their characteristics,
particle size, surface morphology, release behavior in vitro, pharmacokinetics
and in vivo biodistributions were researched. In vitro and in vivo tumor
inhibition effects were systematically investigated. Furthermore, the hemolysis
and acute toxicity of PTX-CMs were also evaluated.
Results: The size of PTX-CMs was 53.61±0.75 nm and the ζ-potential was
–19.73±0.68 mV. PTX was released much slower from PTX-CMs than PTX-Ms in vitro.
Compared with PTX-Ms, the cellular uptake of PTX-CMs was significantly reduced
in macrophages and significantly increased in human cancer cells, and
therefore, PTX-CMs showed strong growth inhibitory effects on human cancer
cells. In vivo, the plasma AUC0–t of PTX-CMs was 1.8-fold higher than that of PTX-Ms, and 5.2-fold
higher than that of Taxol. The biodistribution study indicated that more
PTX-CMs were accumulated in tumor than PTX-Ms and Taxol. Furthermore, the
significant antitumor efficacy of PTX-CMs was observed in mice bearing BEL-7402
hepatocellular carcinoma and A549 lung carcinoma. Results from drug safety
assessment studies including acute toxicity and hemolysis test revealed that the
PTX-CMs were safe for in vivo applications.
Conclusion: These results strongly revealed that NaC-mPEG-PDLLA micelles can
tumor-target delivery of PTX and enhance drug penetration in tumor, suggesting
that NaC-mPEG-PDLLA micelles are promising nanocarrier systems for anticancer
drugs delivery.
Keywords: sodium cholate, polymeric micelles, enhanced, tumor-targeting
delivery