108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肽调控下的氧化石墨烯纳米带等离子体纳米催化分析平台可方便灵敏地用于人体绒毛膜促性腺激素检测
Authors Liang A, Li C, Li D, Luo Y, Wen G, Jiang Z
Received 19 August 2017
Accepted for publication 10 November 2017
Published 12 December 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 8725—8734
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S149536
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
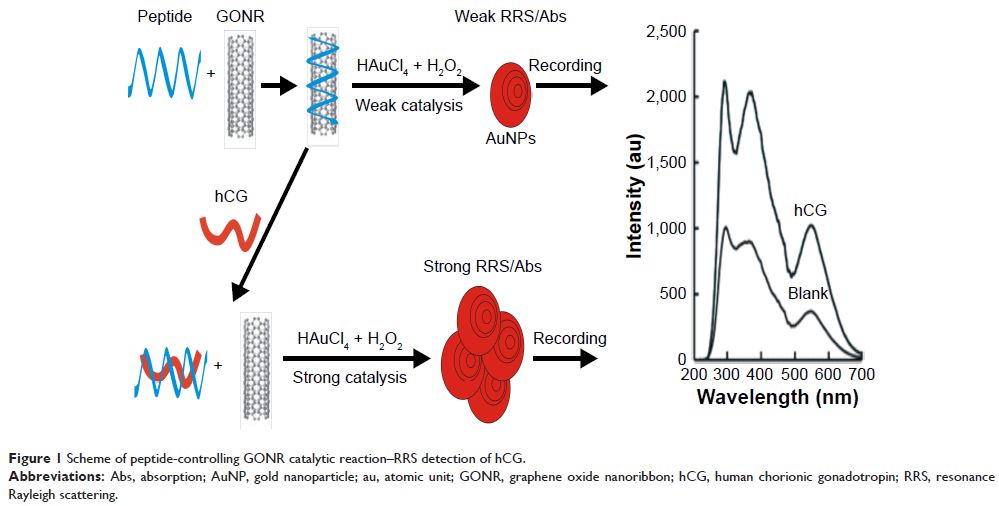
Abstract: The nanogold reaction between HAuCl4 and citrate
is very slow, and the catalyst graphene oxide nanoribbon (GONR) enhanced the
nanoreaction greatly to produce gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) that exhibited
strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption (Abs) at 550 nm and
resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) at 550 nm. Upon addition of the
peptide of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the peptide could adsorb on the
GONR surface, which inhibited the catalysis. When hCG was added, peptides were
separated from the GONR surface due to the formation of stable peptide–hCG
complex, which led to the activation of GONR catalytic effect. With the
increase in hCG concentration, the RRS and Abs signal enhanced linearly. The
enhanced RRS value showed a good linear relationship with hCG concentration in
the range of 0.2–20 ng/mL, with a detection limit of 70 pg/mL.
Accordingly, two new GONR catalytic RRS/Abs methods were established for
detecting hCG in serum samples.
Keywords: nanocatalysis,
graphene oxide nanoribbon, peptide regulation, hCG, RRS