108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:miR-149* 在乳腺癌中通过靶向 GIT1 来抑制体外细胞增殖和转移以及体内肿瘤生长
Authors Dong Y, Chang C, Liu J, Qiang J
Received 18 June 2017
Accepted for publication 31 August 2017
Published 11 December 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5873—5882
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S144280
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
***本文章已被撤回***
Abstract: Breast cancer remains a major cause of cancer-related death in women
worldwide. Dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) is involved in the initiation
and progression of breast cancer. Moreover, it was found that GIT1 was widely
involved in the development of many human cancers. Herein, we aimed to
investigate the expression changes of miR-149* and GIT1 and the functional
effects of miR-149*/GIT1 link in breast cancer. Quantitative reverse
transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot (WB) were
used to examine the expression levels of miR-149* and GIT1. Dual luciferase
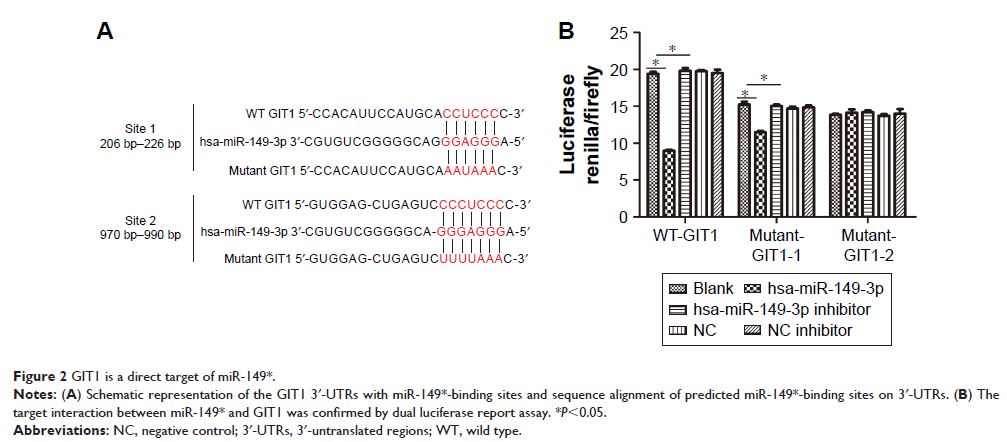
reporter assay was utilized to confirm the target interaction between miR-149*
and GIT1. The biological functions, including cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration, of miR-149* and GIT1 were determined by MTT assay and Transwell
assays, respectively. Eventually, the tumor xenograft model in nude mice
injected with stable transfected MDA-MB-231 cells was established to verify the
effects of miR-149* and GIT1 on tumor growth. Our results showed that miR-149*
expression was decreased, whereas GIT1 expression was increased in clinical
samples of breast cancer. Based on the inverse expression trend between
miR-149* and GIT1, we further demonstrated that miR-149* indeed directly
targets GIT1. Subsequently, it was observed that inhibition of miR-149*
significantly promoted cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, but the
ability of cell proliferation, invasion, and migration was obviously declined
after silencing of GIT1 in MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with miR-149* mimic
and/or si-GIT1. Finally, it was also found that elevated miR-149* decelerated
the tumor growth, while restored GIT1 accelerated the tumor growth in nude mice
after 35 days of tumor xenograft. Collectively, these findings concluded
that miR-149* might exert a tumor suppressive role in breast cancer by
targeting GIT1.
Keywords: microRNA 149*,
miR-149*, G protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein 1, GIT1,
tumor suppressive role, breast cancer